-
Sustainability at Fujitsu Group
- Sustainability Management in the Fujitsu Group
- GRB(Global Responsible Business)Goals and Achievments for FY2022
- GRB(Global Responsible Business)Goals for FY2025
- Fujitsu's accessibility
- Stakeholder Engagement
- United Nations Global Compact
- SDG-related Activities in Fujitsu
- External Recognition and Awards
-
Global Responsible Business
- Environment
-
- Environmental Management
- The Fujitsu Group Environmental Vision on Climate Change
- Living in Harmony with Nature (Conservation of Biodiversity)
- Environmental Action Plan
- Environmental Data
- Environmental Communication
- Environmental Social Activities
- Disposal and Recycling of ICT products
- Environmental Considerations in ICT Products
- Governance
-
Data and Documents
- Fujitsu Group Sustainability Data Book 2024
- Social, Governance and Environmental data
- Independent Assurance Report

- GRI Standards / United Nations Global Compact (UNGC) principles Comparison Table
- SASB Standards Comparison Table
- Sustainability Information Disclosure Framework
- Link to regions responsible business reports
- Contact
- Sitemap
Activities towards Global Responsible Business (GRB) Environmental Goals
Introduction
Climate change is a global issue that impacts the sustainability of society, and it is closely related to water and resource recycling issues. Engaging in global environmental conservation is essential for achieving our Purpose. The Fujitsu Group does its utmost to reduce environmental impact and minimize risks throughout the value chain, and we contribute to the realization of a sustainable society by solving environmental issues together with our customers.
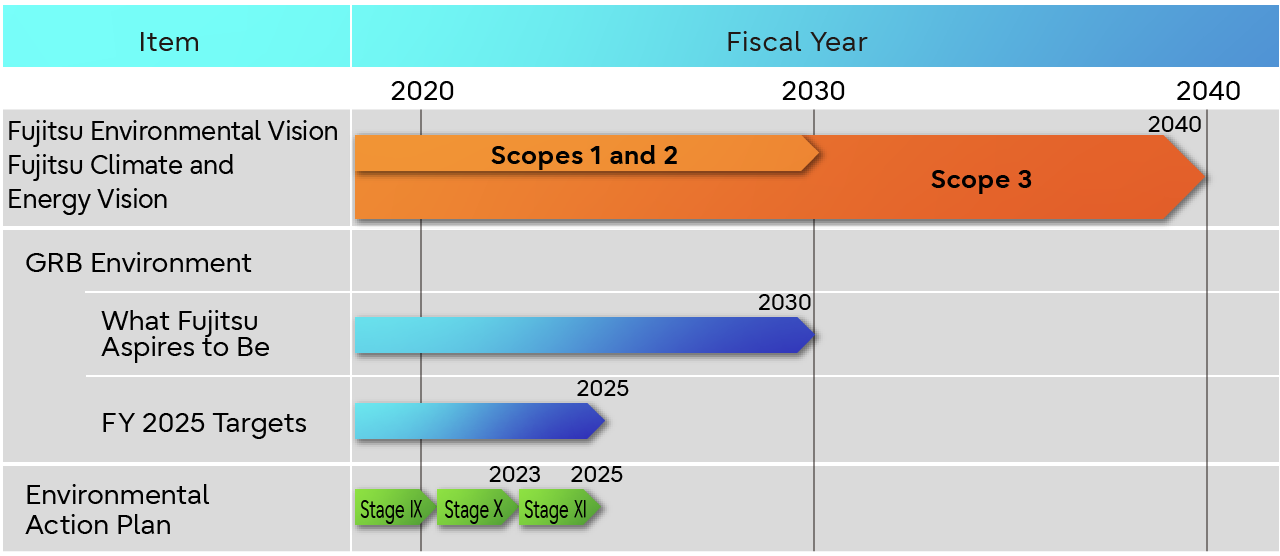 Environmental Vision, Targets, and Other Milestones Achievement Timeline
Environmental Vision, Targets, and Other Milestones Achievement Timeline
To Reduce GHG Emissions in Accordance With 1.5℃ Target
Updating Medium- and Long-term Goals
In May 2017, the Fujitsu Group formulated the Fujitsu Climate and Energy Vision as our environmental vision. In August 2017, we acquired Science Based Target (SBT) initiative validation (2℃-aligned) for our reduction target by 2030. As the movement toward carbon neutrality accelerated, we reconsidered the role that the Fujitsu Group must fulfill, and in April 2021 we raised our GHG emissions reduction target for 2030 from a 33% reduction compared to FY2013 to a 71.4% reduction. This reduction target has been validated as 1.5℃-aligned by SBTi.
In order to accelerate decarbonization in the global community together with our supply chain, we have moved up the Scope 1 and 2 targets deadline for 100% reduction by 20 years from the previous FY2050 to FY2030. Furthermore, we have decided to aim for Net-Zero emissions in the entire value chain, including the supply chain (Scope 3), by FY2040.
To ensure these targets, we will follow the Fujitsu Group Environmental Action Plan (Stage XI) that we created as our activities through FY2025.
(Our Net-Zero target for FY2040 from the base year of FY2020 has been validated by the SBTi in June 2023.)
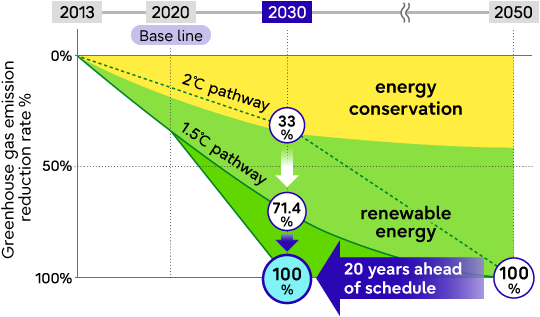 Emission reduction of Fujitsu Group (Scope 1 and 2)
Emission reduction of Fujitsu Group (Scope 1 and 2)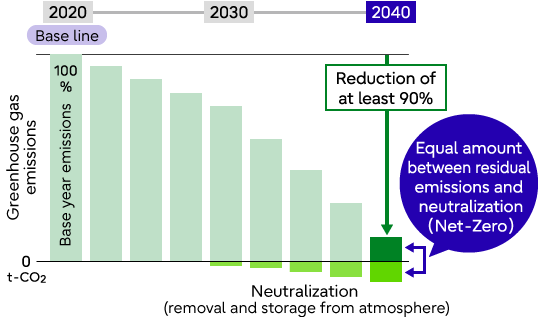 Emission reduction throughout the value chain (Scope 3)
Emission reduction throughout the value chain (Scope 3)Roadmap to Net-zero
Initiatives for Achieving Goals
Since 2018, the Fujitsu Group has been a member of the international initiative RE100, which aims to popularize and expand renewable energy.
Previously, we focused our sites on Europe and the United States. In April 2021, however, in anticipation of full-scale introduction in Japan, we switched all electricity used in the Fujitsu Technology Park (former Kawasaki Plant), the largest scale in the Fujitsu Group, to renewable energy as Fujitsu’s flagship model.
Furthermore, in April 2022, Fujitsu Australia signed the largest renewable energy power purchase agreement (PPA) in the Group, accounting for approximately 47% of its FY2023 annual power consumption. We will continue to systematically procure power from renewable sources and proactively invest in power sources with additional potential, such as power purchase agreements (PPAs), to help expand the use of renewable energy in society as a whole.
 Exterior of Fujitsu Technology Park (former Kawasaki Plant)
Exterior of Fujitsu Technology Park (former Kawasaki Plant)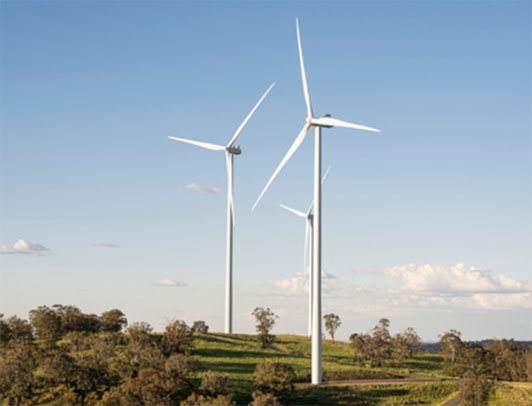 Sapphire Wind Farm
Sapphire Wind Farm
Largest wind farm in New South Wales operated by CWP Renewables
Avoiding Risks Associated with Business Activities and Minimizing Environmental Impact
For more information, click here
Examples of How Our Business Helps Solve Environmental Issues for Customers and Society
For more information, click here


