-
Sustainability at Fujitsu Group
- Sustainability Management in the Fujitsu Group
- GRB(Global Responsible Business)Goals for FY2025
- GRB(Global Responsible Business)Goals and Achievments for FY2022
- Fujitsu's accessibility
- Stakeholder Engagement
- United Nations Global Compact
- SDG-related Activities in Fujitsu
- External Recognition and Awards
-
Global Responsible Business
- Environment
-
- Environmental Management
- The Fujitsu Group Environmental Vision on Climate Change
- Living in Harmony with Nature (Conservation of Biodiversity)
- Environmental Action Plan
- Environmental Data
- Environmental Communication
- Environmental Social Activities
- Disposal and Recycling of ICT products
- Environmental Considerations in ICT Products
- Governance
-
Data and Documents
- Fujitsu Group Sustainability Data Book 2024
- Social, Governance and Environmental data
- Independent Assurance Report

- GRI Standards / United Nations Global Compact (UNGC) principles Comparison Table
- SASB Standards Comparison Table
- Sustainability Information Disclosure Framework
- Link to regions responsible business reports
- Contact
- Sitemap
Intellectual Property (IP) Strategy to Support Fujitsu's Purpose
Policy (IP Management and Corporate Value)
Fujitsu’s Purpose is to make the world more sustainable by building trust in society through innovation. To achieve this, the aim of our intellectual property management policy is to contribute to innovation and new value creation in the Fujitsu Group by strategically building and utilizing intellectual capital, including our technology, our brand and our designs.
Intellectual property management has two facets. One is the construction of an intellectual property portfolio including prosecution for the intellectual capital already held by the Fujitsu Group and then using that portfolio to create new value. The other facet is risk management, which consists of lowering the incidence of risks likely to diminish our corporate or social value, primarily through measures that promote respect for and prevent violations of our rights and those of third parties.
Contributing to Value Creation
We are progressing and appropriately managing the acquisition of the rights to the technology developed by the Fujitsu Group and to the designs and brands created to deploy that technology in the community. This expands our opportunities for generating licensing income, better differentiates our offerings from the technologies and services provided by competitors and maintains or enhances the competitive advantage of Fujitsu Group technologies and services.
We are also assisting with the search for new growth opportunities by investigating, analyzing and sharing information on a wide range of global technology trends, including the status of patent applications in strategically important areas for the Fujitsu Group. Open Source Software (OSS) is an indispensable resource for digital services, and Fujitsu is an active participant in the OSS community, helping to create environments that promote innovation and build a value co-creation ecosystem by formulating rules for the use of intellectual property.
Reducing the Risk of Value Loss
One important way to reduce the risk of losing corporate value by protecting intellectual property. Third party violations of rights held by the Fujitsu Group not only obstruct the progress of our business strategy, they also have the potential to negatively impact customers’ trust in the Fujitsu brand in a competitive environment. For this reason, we constantly monitor for violations of our rights, and where a proposal is discovered that could potentially cause a rights violation, we immediately put in place appropriate countermeasures.
Fujitsu’s Code of Conduct which, together with our Purpose and Values makes up the Fujitsu Way, clearly states our commitment to respecting and protecting intellectual property and respecting the intellectual property rights of others, just as they respect our own acquisition of rights to intellectual capital. We are formulating Rules for Handling Intellectual Property Rights that link this Code of Conduct to specific actions, and these rules are being applied to Fujitsu and Group companies in Japan that undertake actions involving intellectual property. We are also working to reduce the risks of violating rights held by third parties through measures such as thoroughly researching patent violation avoidance, careful OSS license management, and responding to in-house consultation requests concerning the terms of intellectual property agreements.
 Contributing to Value Creation and Reducing the Risk of Value Damage
Contributing to Value Creation and Reducing the Risk of Value Damage
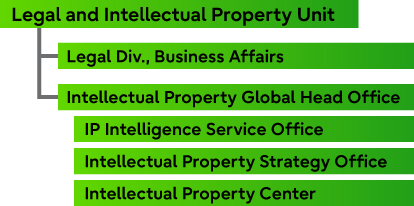
Structure of the Intellectual Property Division (Intellectual Property Global Head Office)
The Intellectual Property Division (the Intellectual Property Global Head Office), which belongs to the Legal and Intellectual Property Unit under the General Counsel, consists of the IP Intelligence Service Office, which supports research laboratories and provides IP landscapes to the front office, the Intellectual Property Strategy Office, which formulates and promotes company-wide intellectual property strategies based on communication with management, and the Intellectual Property Center, which implements intellectual property portfolio construction. In addition to collaborating within each division, the Business & Legal Department promotes intellectual property activities for business producers and SEs, and also collaborates with Fujitsu Techno Research Ltd., which provides intellectual property-related services, to execute intellectual property management.
The formulation of IP management strategy and policy for the activities of the Intellectual Property Division is not limited solely to the Division itself, but is undertaken in collaboration with the Technology Units headed by the Chief Technology Officer (CTO) and Chief Portfolio Officer (CPO) and with the responsible IP strategy managers within the Business Units. In this way, IP management is integrated with our broader management strategy, technology strategy, and business portfolio strategy. In addition, at meetings of the Independent Directors & Auditors Council, which includes external directors and auditors, the Head of the Legal and Intellectual Property Unit reports on the strategy and progress of intellectual property management and provides opportunities for discussion with management.
Group-wide Global Collaboration
Fujitsu has developed an intellectual property governance structure to make the best possible use of its intellectual capital throughout the Fujitsu Group. This ensures that IP-related activities undertaken by Group companies in Japan are integrated. Where a company undertakes independent IP activities as a partial exception, a reporting line is set up and the activity is conducted through close collaboration. Globally, including the utilization of the reporting line, periodic meetings are held involving regional IP managers from the 5 regions of Europe, India, China, Australia and the United States. Additionally, through intellectual property support for research facilities established in another 8 countries around the world to ensure that all IP management conforms to the realities of global business.
Linkage with Technology Strategy and Business Portfolio Strategy
Fujitsu’s stated purpose is: “To make the world more sustainable by building trust in society through innovation”, and our key strategies have sustainability as their starting point. One of the key strategies for the Intellectual Property Division is its Technology strategy, which is to enhance its core technologies with AI as the focus. Taking a structured approach to progressing Fujitsu’s IP activities linkage with our technology strategy and business portfolio strategies helps to maintain and strengthen the Fujitsu Group’s competitive advantage and acquire new business opportunities. In intellectual property activities, in order to achieve competitive superiority, we are strengthening the collaboration between the intellectual property division and the research division, analyzing the strengths of technologies under development in the market from intellectual property information, and feeding back the results from the intellectual property division to the research division. We are also promoting initiatives by identifying areas where international standardization and Open Source Software (OSS) should be actively utilized. Furthermore, in order to enhance the added value of Fujitsu Uvance's offerings, we will deepen the collaboration between the intellectual property division and the business division to promote the enhancement of our offerings through R & D technology.
 Organization of the Intellectual Property Division
Organization of the Intellectual Property Division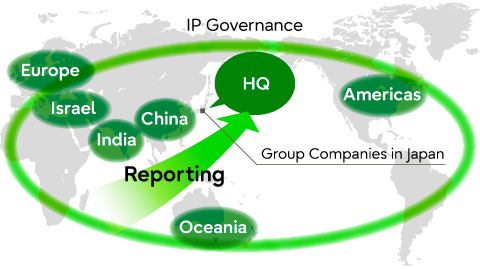 Group-wide Global Collaboration
Group-wide Global CollaborationInitiatives
Fujitsu’s purpose is: “To make the world more sustainable by building trust in society through innovation”, and we pursue our key strategies with sustainability as the starting point, as set out in the Medium-Term Management Plan released in May 2023. In terms of investment in intellectual property, Fujitsu is building an IP portfolio intended to create added value in our services business and is enhancing AI-centered technologies as part of our Technology strategy, one of our key strategies. We are also engaged in leveraging IP for co-creation, including collaboration to help achieve the SDGs under the FUJITSU Technology Licensing Program™ for SDGs. The Company is also engaged in using OSS, international standardization and rulemaking to establish social rules that engender trust and confidence in deploying Fujitsu’s advanced technologies, and strategic initiatives to support the Key Focus Areas from a brand and design perspective.
The following section highlights examples of intellectual property activities including construction of patent portfolios based on technology strategy, utilization of intellectual property to solve societal challenges, and international standardization and rulemaking.
IP Activity Examples
Creation of Intellectual Property
Patent portfolio construction based on Technology Strategy
Under our technology strategy of concentrating R & D resources on Fujitsu Uvance and other five Key Technologies (KT) centered on AI, which is essential for digital services, Fujitsu Group is increasing the share of the five KTs in our patent portfolio. In particular, the number of patent applications for AI-related technology, which has accumulated research and development since the 1980s, ranked first in Japan in fiscal 2023, following fiscal 2022.
In addition to the core technologies that have been Fujitsu’s strength to date, Fujitsu is currently focusing on patent prosecution of applied AI technologies. Applied technologies refer to technologies fuse core technologies with knowledge about specific industries and applications, such as those implemented in Fujitsu Uvance's offerings, or technologies fuse AI with other four KTs technologies. Prosecution of applied technologies is linked with our business strategy to accelerate the integration of the five AI-based KTs with Fujitsu Uvance. We are working to build an applied technology patent portfolio in line with our business strategy to offer Fujitsu Kozuchi, the AI platform announced in March 2024, as part of Fujitsu Uvance.
 Percentage of annual patent applications at Fujitsu
Percentage of annual patent applications at Fujitsu
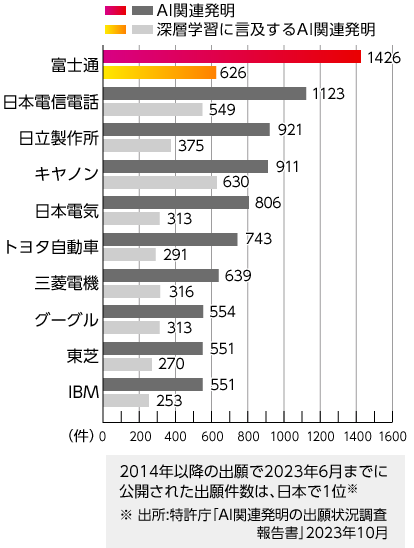 Number of Patent Applications for AI-related inventions by applicant (Japanese text only)
Number of Patent Applications for AI-related inventions by applicant (Japanese text only)
Utilization of Intellectual Property to Solve Social Issues
Promotion to Solve Social Issues by licensing Fujitsu technology to other companies
Fujitsu is promoting technology solutions to solve social issues, by offering Fujitsu technology to other companies.
In November 2023, Fujitsu agreed to license its Topological Data Analysis (TDA), a Fujitsu-developed AI technology that automatically creates an AI model for detecting abnormalities in time-series data, to US startup Delight Health, in exchange for rights to newly issued shares in the company. Under the license, Delight Health will use Fujitsu's TDA technology to establish an advanced delirium detection system currently under development that accurately predicts the onset of delirium, with the goal of receiving Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval by 2024 to help patients suffering from delirium, a serious condition that affects the elderly in particular.
By offering this kind of licensing scheme, the IP Division plans to further explore opportunities to accelerate solutions to social issues.
- Fujitsu Research’s TDA Technologies
- Fujitsu to license Topological Data Analysis technology to Delight Health, a Bay Area startup focused on providing innovative mental health solutions
Standardization and Rule-making
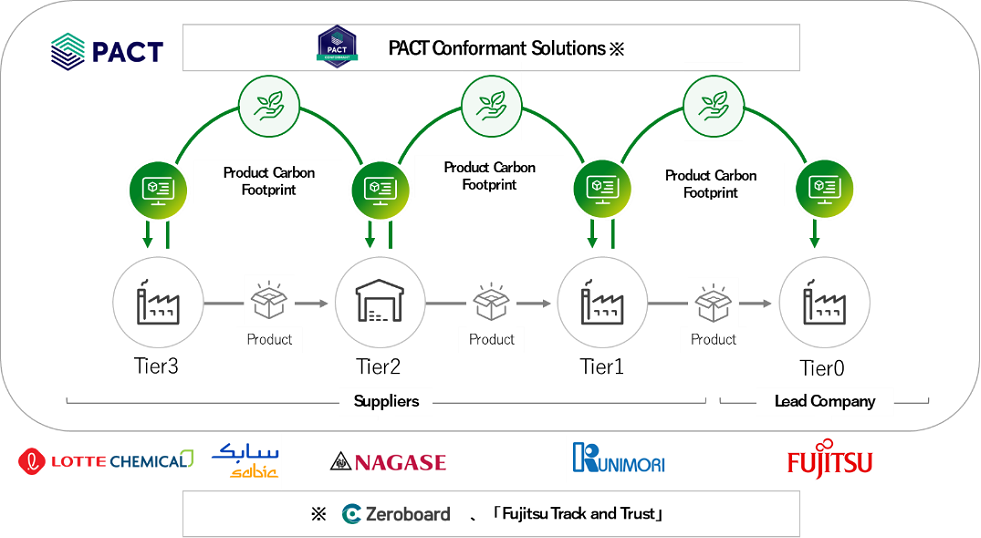
World’s First Successful Visualization of CO2 Emissions across an entire Supply Chain
Fujitsu announced in September 2023 that it had succeeded in the world’s first visualization of CO2 emissions throughout its supply chain through participation in the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD)’s Partnership for Carbon Transparency (PACT) Implementation program.
To achieve carbon neutrality, CO2 emissions must be reduced not only in one company but also across the entire supply chain. For this purpose, it is necessary to calculate the product carbon footprint (PCF) of each component in cooperation with component suppliers for the products, and to link data between companies. As a PACT member, Fujitsu participated in rule-making about PCF calculation methods and the technical specifications for data exchange.
Under the demonstration program, Fujitsu collaborated with Nagase & Co., Ltd, Zeroboard Inc. and other companies, to calculate CO2 emissions for the entire supply chain by linking PCF data among the companies using Fujitsu Track and Trust, a PACT-compliant solution for the supply chain of Fujitsu notebook PC manufacturing.
Fujitsu plans to collaborate with industry organizations and stakeholders including WBCSD to contribute to data exchange between companies and standardization of methodologies in the future. This know-how will be offered as an ESG managed platform service and a digital supply chain service under Fujitsu Uvance.
 Fujitsu PACT program
Fujitsu PACT program
“Ontenna” User Interface – Feeling sound
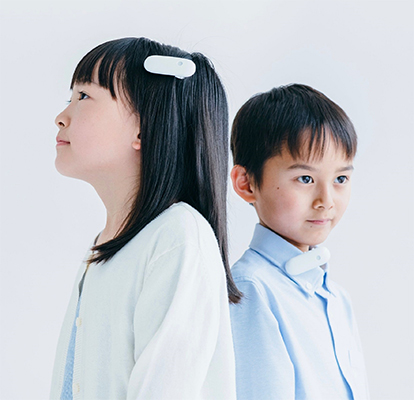 Image of wearing "Ontenna"
Image of wearing "Ontenna"
A mixed-IP strategy to support solutions to societal challenges
Ontenna is a radically new user-interface device that can be worn on the hair, earlobe, collar, cuff, etc., enabling the wearer to pick up tonal characteristics through vibration and light. It was developed in collaboration with the Deaf and the hard-of-hearing to enable a future that they can enjoy together with the hearing.
Ontenna is characterized by a gently rounded shape that does not feel unpleasant as it can be worn like a hairpin. Fujitsu has applied for and registered design patents for the main body, the battery charger, and the controller that can control multiple Ontenna devices, and has also registered the shape of the main body as a 3D trademark. Fujitsu has also applied for and registered patents for Ontenna's charging method and communication system, using a mixed-IP strategy to protect the main body and peripheral devices.
Ontenna was awarded the “Imperial Invention Prize” in the 2022 National Commendation for its design patent. It has also won several other awards including the 2019 Good Design Award “Gold Prize,” the IAUD International Design Award “Grand Prize,” and the Local Invention Award from the Commissioner of the Japan Patent Office, earning high acclaim from both inside and outside of Fujitsu. More than 80% of all Schools for the Deaf in Japan have introduced Ontenna, and its use in music and physical education classes is expanding rapidly as a tool for providing a new appreciationexperience.
- Ontenna, Which Enables You to Feel Sound with Your Body and Enjoy It with Those around You
- Ontenna
- Imperial Invention Prize Awarded to the Design for a Wearable Device Design That Senses Sound as Vibration or Light (Japanese text only)
Solving Societal Issues through Co-creation
FUJITSU Technology Licensing Program™ for SDGs
Fujitsu is promoting the FUJITSU Technology Licensing Program™ for SDGs, an initiative that encourages companies and academic institutions to use the Group’s intellectual property including patents and expertise as a key means of contributing to SDGs to make the world more sustainable through innovation.
Through collaboration under WIPO GREEN, a framework for technology transfer for environment-related technologies, intellectual property matching activities at national and local governments, financial institutions and universities, intellectual property creation education in collaboration with educational institutions, and brand design for an inclusive society, we are expanding opportunities for Fujitsu Group's technologies to be used in society and contributing to environmental conservation, well-being and economic growth. We believe that continuing these efforts will contribute to the formation of a variety of intangible assets, including the recognition of the Fujitsu Group in the global society and the incentives for employee innovation.
 FUJITSU Technology Licensing Program™ for SDGs
FUJITSU Technology Licensing Program™ for SDGs
Specifically, by introducing our patented technology at intellectual property matching meetings hosted by local governments and financial institutions, we licensed our technology to many companies and universities to create a variety of new products and services that solve social issues. We also organized intellectual property workshops for students using our technology as theme of our activities to foster future innovators.
 IP Workshop in Saitama Prefecture
IP Workshop in Saitama Prefecture IP Workshop in Beppu City
IP Workshop in Beppu CityAnother example of technology licensing outside Fujitsu
Solving Societal Issues through Design
Ekimatopeia: making train use safer
Ekimatopeia was developed in 2021 by Fujitsu in collaboration with East Japan Railway Company (JR East) and Dai Nippon Printing (DNP) in a workshop with Kawasaki Municipal School for the Deaf around the theme of "Future Commute to School." It is a device that tested repeatedly with the aim of creating an experience that is easy for anyone to use and that makes daily train use enjoyable.
Announcements inside the station platform and the environmental sound of the train collected by the microphone are analyzed by AI, converted into letters and sign language in real time, and displayed on the dedicated display. Onomatopoeia animation is used to transcribe environmental sounds, and a video by JR East station staff and DNP's "emotion-expressing font" are used for sign language. These are displayed according to the sound information of each station platform. Fujitsu’s FX1000 supercomputer was used in the AI development.
Design Features :
Announcements and sounds around the information display installed in the station can be displayed as text on this display monitor. Unique fonts are used for the characters displayed on the monitor, and the movement and expression of the characters are elaborated.
Design Impact :
Station announcements and audio can be displayed on the screens so that they can be easily understood by deaf people. Emergency announcements in the station and train delay information can also be displayed. Also, when station audio is not being displayed, the screen can display advertising.
Protection by design right :
The design is protected by design right to prevent this idea, conceived by the inventors together with student participants of the school for the deaf, from being replaced by competitors. Design right is also protected because rounded designs have novelty and may increase opportunities for Fujitsu's technical capabilities and media exposure.
- Fujitsu's Ekimatopeia wins the METI Minister Award at the 17th Kids Design Awards in Japan
- Ekimatopeia
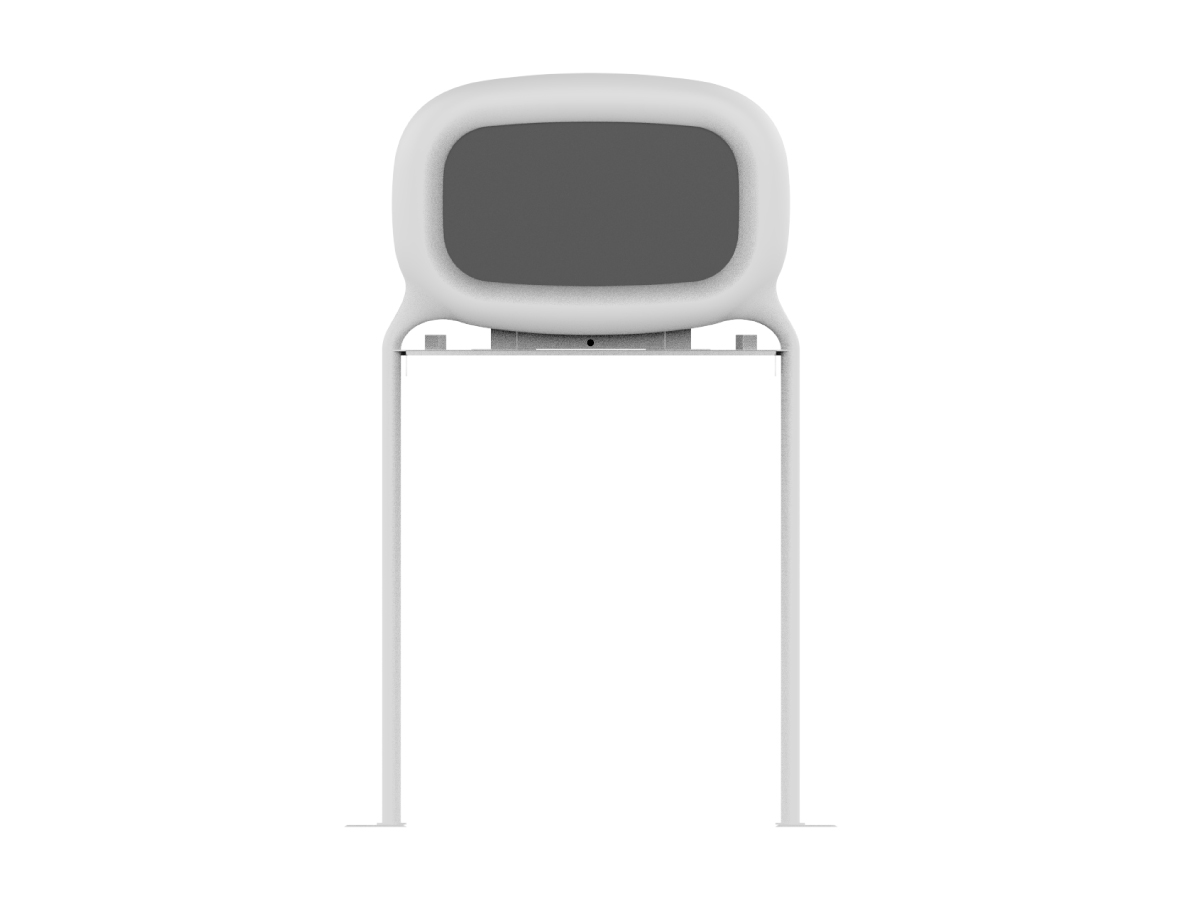
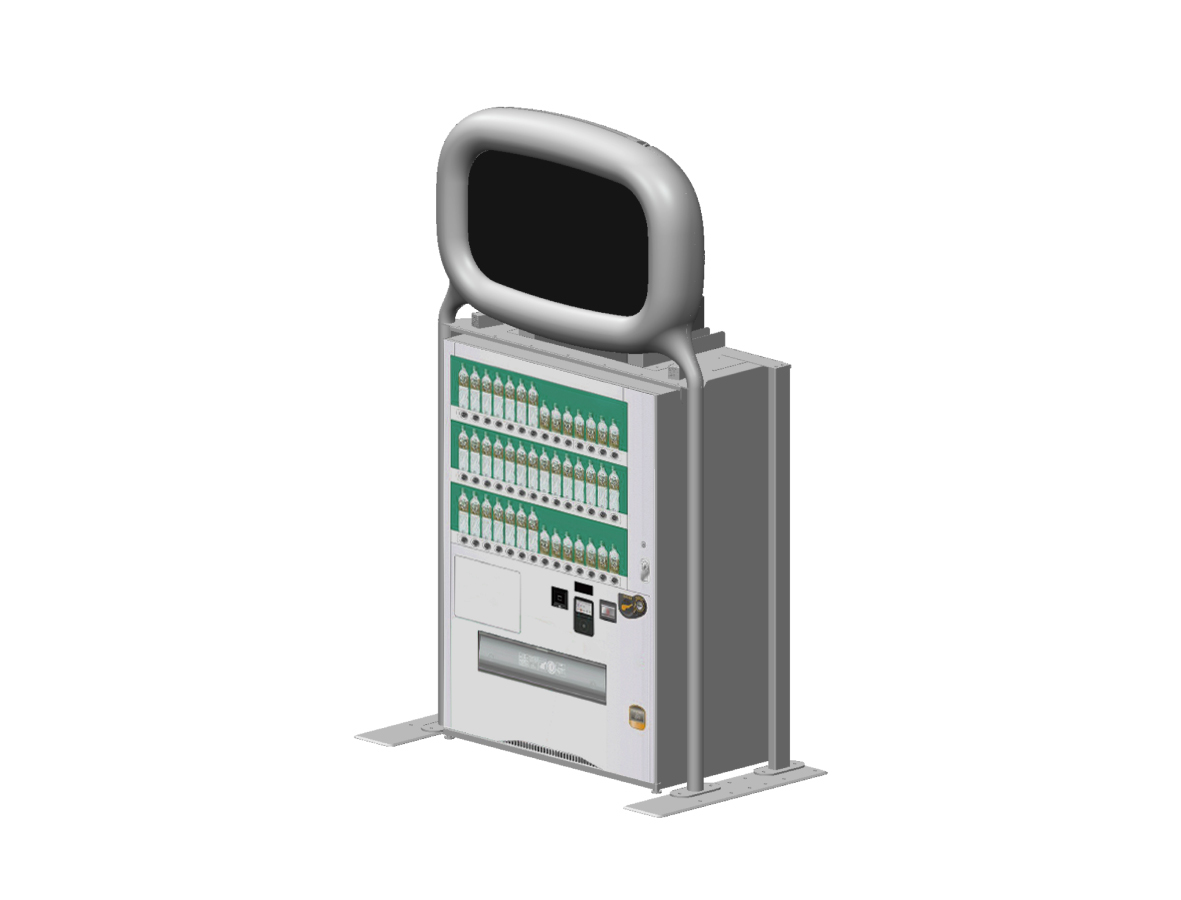



<Design> Design registration no. 1729569


