-
Nachhaltigkeit bei der Fujitsu Gruppe
-
Global Responsible Business
- Governance
-
Daten und Dokumente
- Fujitsu Group Sustainability Data Book 2023
- Angaben zu Beschäftigung, Umweltschutz und Governance
- Independent Assurance Report
- GRI-Standards / Prinzipien des Global Compact der Vereinten Nationen (UNGC) Vergleichstabelle
- SASB Standards Vergleichstabelle
- Rahmen des Datenbuchs zur Nachhaltigkeit
- Link zu den Nachhaltigkeitsberichten (CSR-Bericht) der Regionen
- Kontakt
- Sitemap
Materiality
Materiality in the Fujitsu Group
The Fujitsu Group revised its approach to Materiality in 2023. We specified Materiality in 2018 under the Basic CSR Policy but have now updated it to encompass Materiality in Management, which incorporates the perspective of delivering value to customers and society through our business activities.
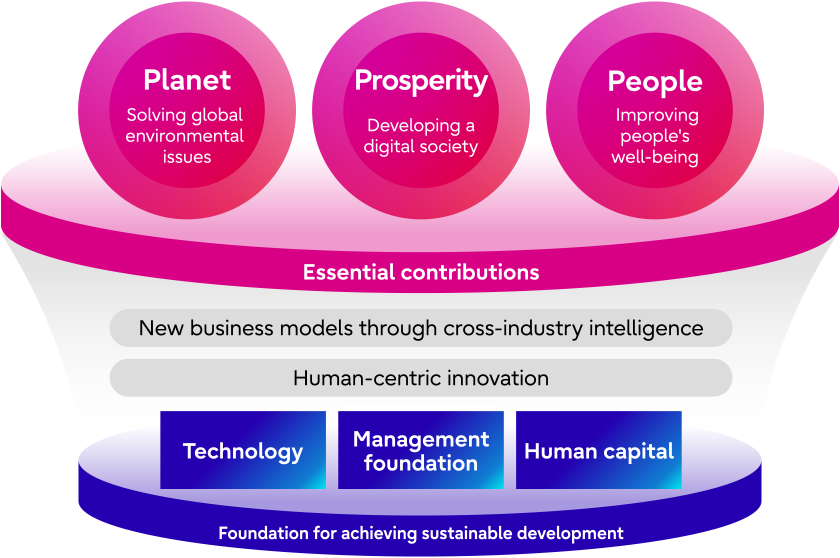
Looking toward 2030, we conducted medium- to long-term evaluations from the perspectives of Fujitsu itself and its stakeholders, and we identified priority issues to be resolved on the path to sustainable growth. These fall under two categories (Essential Contributions and Foundation for Achieving Sustainable Development). In the first category of Essential Contributions, we will leverage the development of Fujitsu Uvance and other businesses to provide customers and society with value that contributes to solving global environmental issues, developing a digital society, and improving people's well-being. Furthermore, we will strengthen our technology, management foundation, and human capital to create the Foundation for Achieving Sustainable Development as the source of value creation for the Fujitsu Group, while supporting the creation of new business models and spurring innovation.
The results of this revised approach to Materiality are being applied to risk management throughout Fujitsu. In the potential risk assessment conducted throughout the Fujitsu Group, issues identified through Materiality assessment are reported as key risks, and "climate change", "human resources and human rights" and "information security" are identified as "main business risks".
And Materiality-related initiatives are recommended as a goal-setting item in the “Executive Performance Management” evaluation system for executives at FUJITSU VP-level and above. The non-financial indicators based on Materiality are being progressively linked to the evaluation indicators for executive remuneration (Executive Director bonuses).
Going forward, we will continue to promote company-wide initiatives related to Materiality, reduce and avoid critical management risks, and maximize business opportunities. In this way, we aim to enhance the corporate value of the Fujitsu Group and contribute to achieving net positives in the areas of environmental issues, digital society, and people's well-being.
Materiality
Materiality
Essential contributions (3 global imperatives, with 11 issues where we will contribute in)
| Planet:
Solving global environmental issuesContribute to creating a future earth where both people and nature can thrive |
|---|
| Climate change (Carbon neutral) |
| Resource circulation (Circular economy) |
| Living in harmony with nature
(Protection and restoration of biodiversity) |
| Prosperity:
Developing a digital societyContribute to creating a trusted digital society where global prosperity and stability are compatible |
|---|
| Maintaining security of information |
| Eliminating the digital divide |
| Leading ethical AI and IT |
| Ensuring a positive work environment and addressing labor shortages |
| Assuring responsible supply chains |
| People:
Improving people's well-beingContribute to improving quality of life and opportunities across society to support the well-being of people |
|---|
| Contributing to healthcare for an improved quality of life |
| Promoting lifelong education and reskilling |
| Improving customer/consumer experience |
Foundation for achieving Sustainable Development (7 issues)
| TechnologyInnovating cutting-edge digital technologies which co-create new opportunities to transform to a sustainable society |
|---|
| Creating and developing cutting-edge innovative technologies |
| Management foundationData-driven management that pre-empts and flexibly responds to the business environment with highly efficient, rapid decision-making |
|---|
| Governance and compliance |
| Risk management |
| Economic security management |
| Digital transformation |
| Human capitalCreating innovation everywhere in society by bringing together agile and versatile people from inside & outside the company |
|---|
| DE&I |
| Well-being and
human resource development |
Materiality Assessment Process
The Fujitsu Group identified Materiality based on the principles of double materiality, whereby the mutual impacts of corporations and the environment and society are taken into account (i.e. both the financial impact of environmental and social issues on Fujitsu and the impact of Fujitsu business activities on the environment and society). Going forward, we will conduct periodic reviews on an annual basis and revise as necessary.
- Step 1
- Organize and Identify Social Issues
- Create a long list of various social issues (163 issues) that will flow from the future megatrends anticipated for 2030 based on the following:
- SDGs
- Evaluations of ESG indices (FTSE, MSCI and DJSI)
- ESG reporting framework (GRI Standards, SASB Standards)
- World Economic Forum (WEF) Global Risk Reports
- Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) Code of Conduct
- World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBSCD), Global Enabling Sustainability Initiative (GeSI) documentation
- Identify 40 social issues by integrating similar items and deleting items with minimal business relevance
- Create a long list of various social issues (163 issues) that will flow from the future megatrends anticipated for 2030 based on the following:
- Step 2
- Prioritization
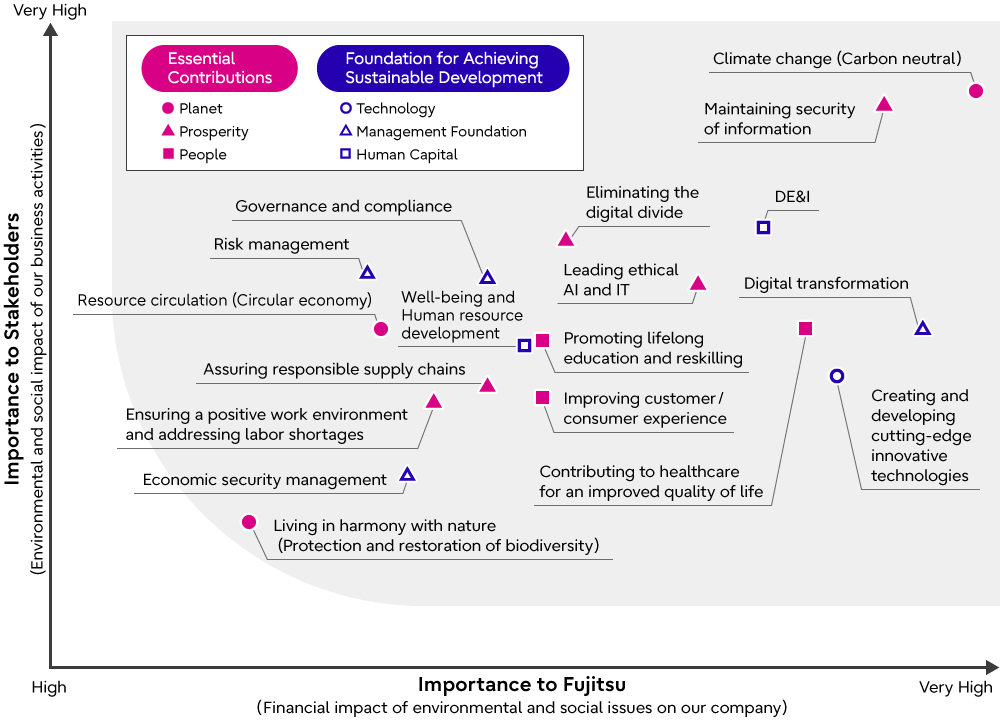
- Conduct surveys, interviews and desktop research with a wide range of internal and external stakeholders based on the identified social issues. In anticipation of future circumstances in 2030, create a draft materiality matrix that prioritizes 25 social issues in terms of the risks and opportunities those issues present. The draft materiality matrix is created by conducting comprehensive assessments and assigning scores to issues from the perspectives of their importance to Fujitsu (financial impact of the environmental and social issues on Fujitsu) and their importance to stakeholders (environmental and social impact of Fujitsu business activities).
- Through personal interviews and meetings of the Sustainability Management Committee, conduct assessments and discuss the validation of the draft materiality matrix in terms of Fujitsu’s distinctiveness (affinity with the Fujitsu brand), and determine the final materiality matrix (18 issues). (This process entails assessments and discussions by Executive Directors and other executives together with reviews by non-executive directors and the Audit & Supervisory Board Members.)
- Organize the materiality concept and then classify and arrange the 18 issues into 2 categories and 6 areas.
Fujitsu and Stakeholder Assessment
Assessment method Details Fujitsu Surveys, interviews Executives - Survey and/or interview a total of 43 executives, including the Sustainability Management Committee, Executive Directors, and other executives.
Fujitsu Way promotion leaders - Survey all 123 Fujitsu Way promotion leaders.
Desktop research - Use internal and external data to quantitatively and qualitatively evaluate the extent of the impact of social issues in terms of sales, costs, reputation, compliance and consistency with business strategy.
Stakeholders Surveys, interviews Employees - Select employees in each of the company-wide (global) divisions at random and survey 3,284 employees in total.
Market (customers and suppliers) *1 - Survey and/or interview company management and middle management working in Fujitsu customer and supplier industries globally (9 countries, 14 industries)
Investors - Survey and/or interview Fujitsu capital markets participants.
Desktop research - Quantitatively and qualitatively assess importance from the perspective of stakeholders based on the survey forms used by representative ESG rating agencies and various other external documents and reports.
- *1A commissioned study conducted by Forrester Consulting on behalf of Fujitsu, August 2022
Materiality Matrix
- Step 3
- Management Approval
- Through the Sustainability Management Committee, discuss and approve materiality and the direction for promoting company-wide initiatives. Materiality as included in the Medium-Term Management Plan is then discussed and approved by the Board of Directors.
- Step 4
- Review
- Review and discuss annually based on changes in the internal and external environment.
- Where necessary, undertake revisions through Steps 1-3.
Approach to Materiality
Taking into account the risks and opportunities posed by materiality, we have discussed our approach for FY2025. Fujitsu will implement measures to address risks, focusing on our internal initiatives, while addressing opportunities by expanding Fujitsu Uvance and other businesses to solve social issues and provide value to customers and society. Moving forward with this approach to materiality will hasten reductions in the negative impacts while promoting greater positive impacts, leading to net positive outcomes for Fujitsu businesses and society.
Planet: Solving global environmental issues -- Contribute to creating a future earth where both people and nature can thrive
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
FY2025 targets
- Scope 1, 2 GHG emissions: 50% reduction (on FY2020 levels)
- Scope 3 GHG emissions (Category 11): 12.5% reduction (on FY2020 levels)
Please also refer to our other environmental targets
| Materiality | Recognition of risks & opportunities *2 | Approaches for FY2025 (main initiatives) |
|---|---|---|
| Climate change
(Carbon neutral) | Risks
| Internal initiatives
|
Opportunities
| Business growth for customers and society
| |
| Resource circulation (Circular economy) | Risks
| Internal initiatives
|
Opportunities
| Business growth for customers and society
| |
| Living in harmony with nature
(Protection and restoration of biodiversity) | Risks
| Internal initiatives
|
Opportunities
| Business growth for customers and society
|
Business Impacts
- Promoting activities that minimize environmental impacts in our areas of business activity, including the supply chain (reducing GHG emissions, saving and recycling resources, protecting biodiversity) can help to reduce or avoid risks such as reputational damage and excessively strict regulatory controls
- With the transition to a more environmentally friendly society, there is increasing demand for minimization of the environmental impacts on each industry’s entire value chain. Expanding businesses that are designed to address environmental issues and create value for the environment can lead to increased financial returns
See TCFD Information Disclosure for more information on the analysis of business impacts from climate change
Societal Impacts
- By developing solutions such as using digital technology to visualize environmental footprints and improve traceability, we can contribute to restoring biodiversity, building a circular economy and a carbon-neutral society, as well as reducing our customers’ environmental impacts
Prosperity: Developing a digital society -- Contribute to creating a trusted digital society where global prosperity and stability are compatible
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
| Materiality | Recognition of risks & opportunities *2 | Approaches for FY2025 (main initiatives) |
|---|---|---|
| Maintaining security of information | Risks
| Internal initiatives
|
Opportunities
| Business growth for customers and society
| |
| Eliminating the digital divide | Opportunities
| Business growth for customers and society
|
| Leading ethical AI and IT | Risks
| Internal initiatives
|
Opportunities
| Business growth for customers and society
| |
| Ensuring a positive work environment and addressing labor shortages | Opportunities
| Business growth for customers and society
|
| Assuring responsible supply chains | Risks
| Internal initiatives (approach to the supply chain)
|
Opportunities
| Business growth for customers and society
|
Business Impacts
- While issues such as insufficient information security measures, ethical problems associated with AI and human rights violations in supply chains can result in outcomes such as loss of trust by customers and society as well as increases in the cost of dealing with such issues, these risks can be minimized by setting up strong governance structures and introducing effective countermeasures
- Our customers and society also face the above issues, as well as problems such as a growing digital divide and worsening labor shortages. With the transition to a digital society, developing businesses aimed at resolving these issues can help to increase our financial returns
Societal Impacts
- By developing solutions such as explainable AI and secure information infrastructure, we can build trusted digital technology into society and help to build a more resilient society where more people can reap the rewards of digital technology
People: Improving people’s well-being -- Contribute to improving quality of life and opportunities across society to support the well-being of people
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
| Materiality | Recognition of risks & opportunities *2 | Approaches for FY2025 (main initiatives) |
|---|---|---|
| Contributing to healthcare for an improved quality of life | Opportunities
| Business growth for customers and society
|
| Promoting lifelong education and reskilling | Opportunities
| Business growth for customers and society
|
| Improving customer/consumer experience | Opportunities
| Business growth for customers and society
|
Business Impacts
- As peoples’ values transition from material wealth to spiritual richness, they will demand more advanced medical treatment, healthcare, education and customer/consumer experiences. Developing human-centric business that help people to enjoy quality lives that are safe and secure can help to increase our financial returns
Societal Impacts
- By providing services that cater to people’s individual healthcare needs and respond to consumption trends while providing them with the upskilling they need for their career plans, we can not only help people live longer, healthier lives, but we can also help build a society where everyone lives a full and happy life where they can maximize their own potential
| Common indicators for essential contributions | FY2025 targets
|
| Common initiatives for essential contributions:
Contribute to global and regional communities |
|
Technology: Innovating cutting-edge digital technologies which co-create new opportunities to transform to a sustainable society
![]()
| Materiality | Recognition of risks & opportunities *2 | Approaches for FY2025 (main initiatives) |
|---|---|---|
| Creating and developing cutting-edge innovative technologies | Risks
| Internal initiatives
|
Business Impacts
- Helping to achieve sustainable business innovation by conducting R&D into the 5 technology areas of Computing, AI, Data & Security, Converging Technologies and Networks and creating digital innovation
Societal Impacts
- Continue supporting sustainable transformation and address customer and social issues by providing comprehensive value that brings together technologies
Management Foundation: Data-driven management that pre-empts and flexibly responds to the business environment with highly efficient, rapid decision-making
![]()
![]()
FY2022 targets
- DX promotion index: 3.5
| Materiality | Recognition of risks & opportunities *2 | Approaches for FY2025 (main initiatives) |
|---|---|---|
| Governance and compliance | Risks
| Internal initiatives
|
| Risk management | Risks
| Internal initiatives
|
| Economic security management | Risks
| Internal initiatives
|
| Digital transformation | Risks
| Internal initiatives
|
Business Impacts
- Failure to maintain a strong management infrastructure and improved management efficiency poses serious risks such as lower productivity and lower levels of social trust. Establishing robust governance structures and introducing effective countermeasures can help to minimize such risks
Societal Impacts
- Failing to maintain a strong management infrastructure and improved management efficiency could also result in losses for customers and suppliers in the business area. Establishing robust governance structures and introducing effective countermeasures can help to minimize these risks
Human Capital: Creating innovation everywhere in society by bringing together agile and versatile people from inside & outside the Company
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
FY2025 targets
- Employee engagement : 75
- The percentage of women in leadership roles: 20%
| Materiality | Recognition of risks & opportunities *2 | Approaches for FY2025 (main initiatives) |
|---|---|---|
| DE&I | Risks
| Internal initiatives
|
| Well-being and Human resource development | Risks
| Internal initiatives
|
Business Impacts
- Boosting investment in human capital, such as through stronger personnel development platforms and personnel portfolios, can assist in extracting the maximum possible value from personnel and increase sustainable value creation and corporate value
Societal Impacts
- Promoting activities to protect diversity and respect for human rights in the supply chain can help to lessen or avoid DE&I-related supply chain risk
- *2Recognition of risks & opportunities was organized and analyzed based on various publicly available information in Step 1 (Organize and Identify Social Issues) of the materiality assessment process.


