- Intellectual
Property TOP - Intellectual Property
Strategy to Support Fujitsu's
Purpose - Intellectual
Property Portfolio - Brands &
Trademarks / Design
& Design Rights - Intellectual Property
Management and
Risk Compliance - International
Standardization
and Rulemaking - Efforts to Utilize
Intellectual Property
for Co-creation - Evaluations from
Third Parties
Intellectual Property Portfolio
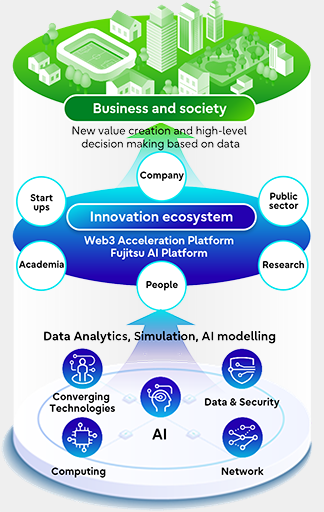
Fujitsu Group Advantages in Five Key Technologies
The creation and utilization of our intellectual property portfolio of the five Key Technologies that are essential for our digital services are priorities in the Fujitsu Group's intellectual property management.
These five Key Technologies are Computing, which enables the processing of massive amounts of data; Network, which supports the use of data and computing power; AI, which supports simulations and decision-making using data; Data & Security, which maintains the safety of all of these; and Converging Technologies, which brings new value to people, organizations, and society by combining technology with humanities and social sciences that are needed when using digital technology. The Fujitsu Group's competitive advantage is not only having high technological capabilities in all the domains of these five Key Technologies but also the ability to connect and combine these technologies to provide digital services.
Going forward, we plan not only to create an excellent intellectual property portfolio by acquiring rights for the technology we develop but also to provide insight and knowledge gained from analyzing patent and market information in the planning stage of developing technology or offerings. We also plan to focus on initiatives for our capability to promote business portfolio strategies and the creation of new business models, such as participation in discussions about approaches to intellectual property appropriate for co-creation with customers, and open innovation with universities and research institutions.
Changes in Our Intellectual Property Portfolio
Since its founding, the Fujitsu Group has made major shifts in its business pillars, from telegraph and telephone communications equipment; to computers (including servers and PCs); to information and communications technology (ICT) services that are at the center of creating core systems for corporations, government agencies, and local governments; and now to cloud-based service-oriented businesses that utilize digital technology.
This shift in the direction of management to services utilizing digital technology, which began in 2018, has changed our intellectual property portfolio. The percentage of the five Key Technologies making up the cumulative number of patents filed after 2018 increased by 9 percentage points, compared with the same number of patents between 2001 and 2017, following the acceleration of development in the domains of AI, Data & Security, and Converging Technologies, in addition to Network and Computing, in which we have held numerous technological assets as core technology since our founding.
Creation of Our Patent Portfolio for the Five Key Technologies
Among our five Key Technologies, the Fujitsu Group has an abundance of intellectual capital in Network and Computing. We are creating a bridgehead in the development of quantum computers, in addition to a mechanism to solve combinatorial optimization problems at high speed (Digital Annealer™). In the "Quantum Computer-related Technology," the 2023 Patent Application Technology Trend Survey Report issued by the Japan Patent Office, We are also ranked first among Japanese companies (ninth in the world). We are a leading global company in the development of 5G (fifth generation) telecommunications technology.
Furthermore, according to an October 2024 survey by the Japan Patent Office, the Group ranked first in Japan in terms of the number of AI-related patent applications, and according to a January 2019 survey by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), the Group ranked sixth in the world in terms of the number of AI-related patent applications. Under these circumstances, the Fujitsu Group is advancing highly unique developments in Explainable AI (Wide Learning™), which realizes collaboration between humans and AI, and the number of patents filed has rapidly increased.
In the Data & Securities domain, we have developed an identity distribution technology that enables users to assess the trustworthiness of online trading partners (IDYX™), reinforcing our related patent portfolio.
Converging Technologies is a domain in which Fujitsu can demonstrate its uniqueness and create new value for people and society through the fusion of digital technology with the humanities and social sciences. A cutting-edge example is an AI technology (Actlyzer™) that recognizes various human actions from images by combining this technology with knowledge from behavioral science.
Number of patents filed for AI-related inventions by applicants (applications filed
since 2014 and published by August 2024)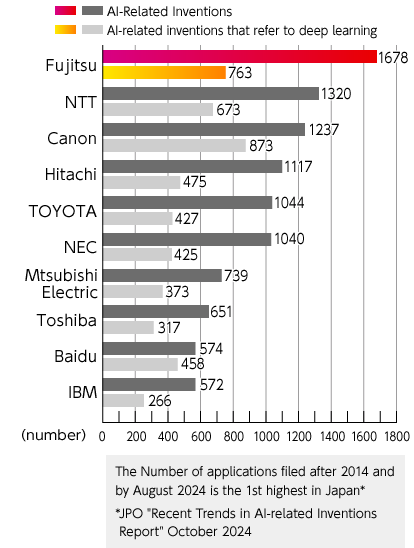
"Quantum Computer-related Technology,"
the 2023 Patent Application Technology Trend Survey Report
Ranking of top patent family applicants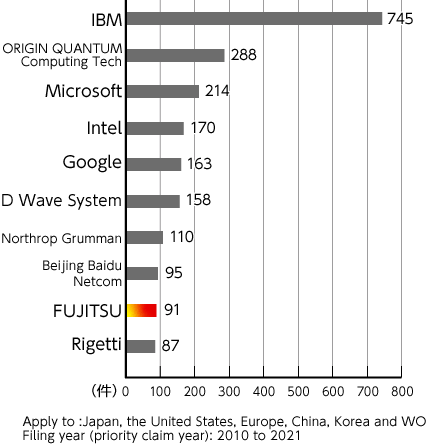
- Fujitsu's Intellectual Property
- Intellectual Property Strategy to Support Fujitsu's Purpose
- Intellectual Property Portfolio
- Brands & Trademarks / Design & Design Rights
- Intellectual Property Management and Risk Compliance
- International Standardization and Rulemaking
- Efforts to Utilize Intellectual Property for Co-creation
- Evaluations from Third Parties
