Features
Feature1 Implementation of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models
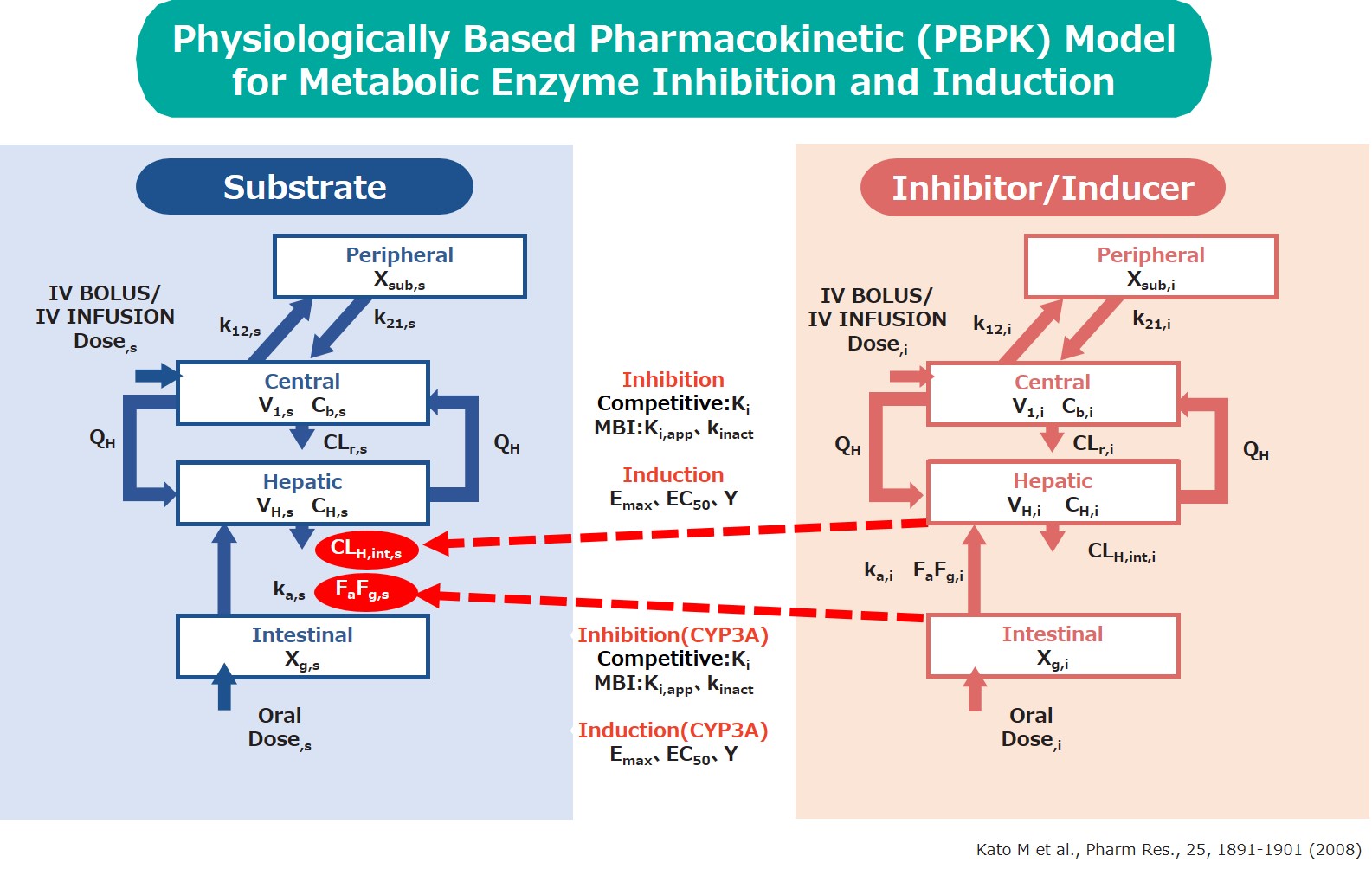
The physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model is used to quantitatively and accurately predict drug interactions.
Available Models
- Inhibition (competitive inhibition/MBI) and induction of hepatic metabolism
- Inhibition (competitive inhibition/MBI) and induction of gut metabolism
- Transporter inhibition
- Hepatic OATPs inhibition
Feature2 Metabolic enzyme inhibition (competitive inhibition/MBI) and induction model
Predict drug interactions via reversible competitive inhibition, irreversible MBI (Mechanism-Based Inhibition) causing deactivation of enzymes, and the induction of metabolic enzymes.
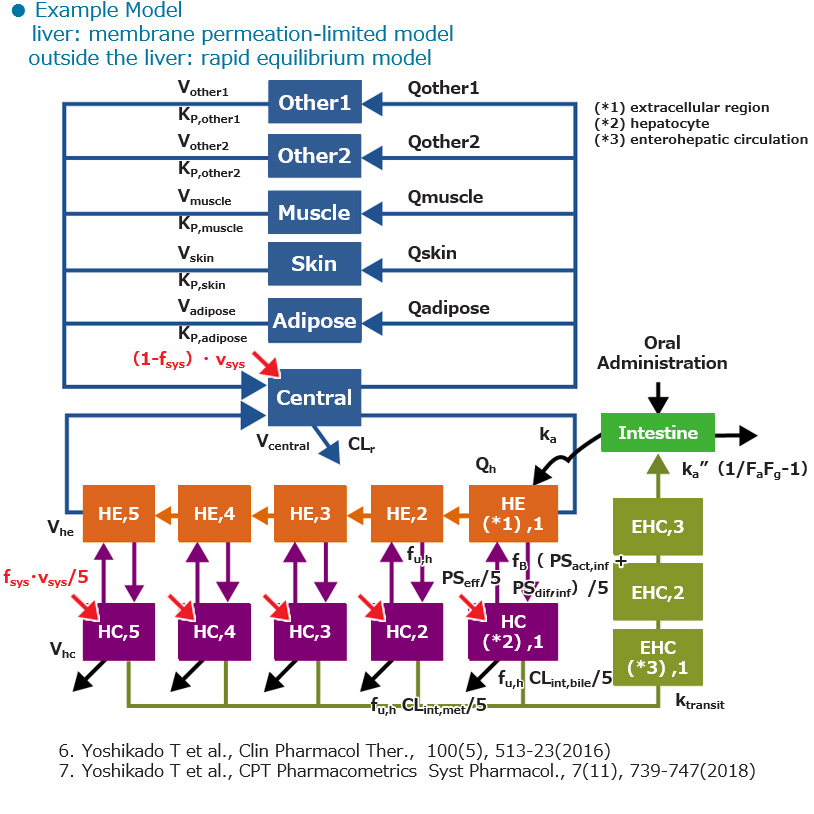
Feature3 Hepatic OATPs Inhibition Model
Predict drug interactions mediated via hepatic OATPs, including prediction of changes in blood levels of endogenous substrates during interactions.
Point
- Considering the distribution of drugs into tissues with relatively large distribution volumes
- Applying a 5-liver model enables us to mimic the dispersion model
- Taking into account the enterohepatic circulation
Feature4 Drug PK Database
The database contains representative substrates, inhibitors and inducers of each major metabolic enzymes, and allows customization and addition of in-house compounds.
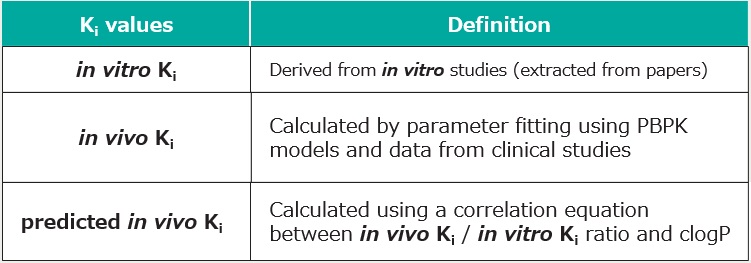
Quantitative prediction of drug interactions due to the inhibition of drug metabolism depends on the inhibition constant (Ki) of the drug. Three types of Ki values are registered in DDI Simulator.
Feature5 Simultaneous inhibition and induction of multiple CYP isoforms
For drugs involving multiple CYP isoforms, it is possible to predict interactions by considering the simultaneous inhibition and induction of CYP isoforms in order to more accurately reflect drug interactions in clinical practice.
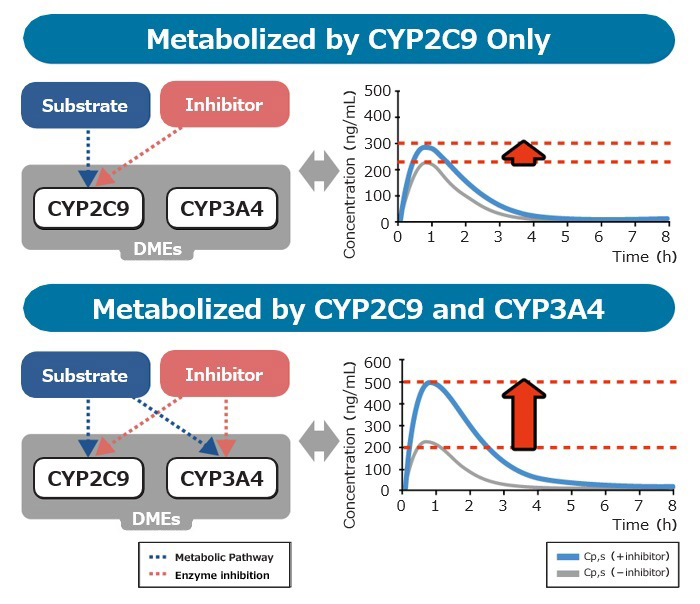
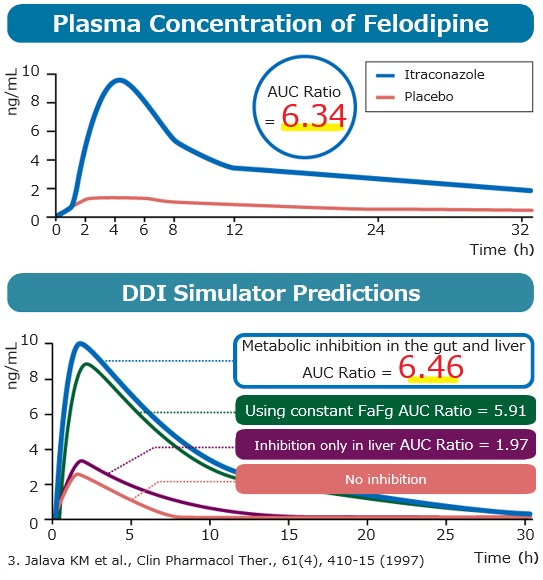
Feature6 Drug Interactions Based on Inhibition & Induction of Gut Metabolism
Allows highly accurate prediction of drug interactions.
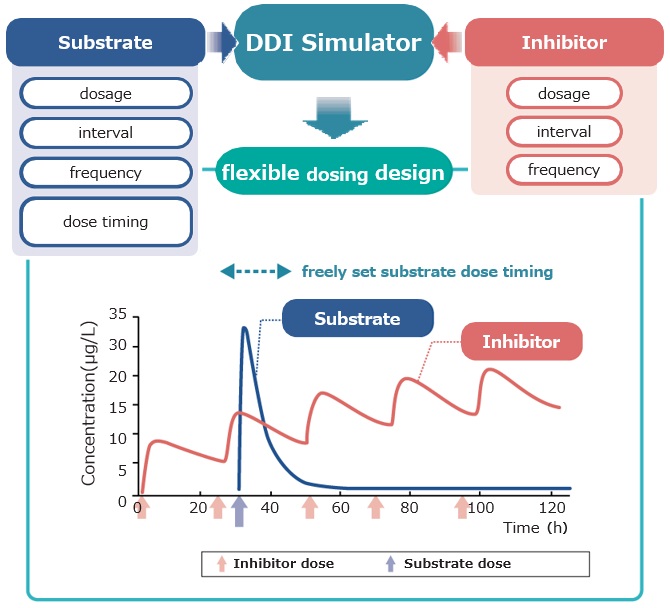
Feature7 Optimizing the dosing schedule to minimize the effects of drug interactions
Dosing schedules can be studied to minimize the impact of drug interactions for each of the substrates, inhibitors and inducers.
The system calculates a steady state of repeated dosing and automatically sets the timing of the substrate to maximize drug interactions.
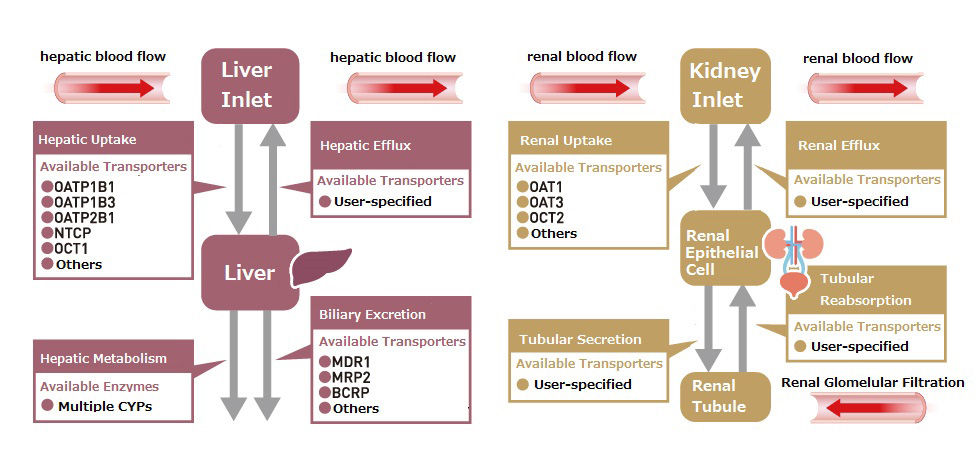
Feature8 Transporter Inhibition Model
Predict drug interactions via inhibition of uptake and efflux transporters in the liver and kidney.
Simulations can also include the effects of competitive inhibition of metabolic enzymes.