Archived content
NOTE: this is an archived page and the content is likely to be out of date.
Fujitsu’s AI Advances Cut Costs for Visual Inspection
News facts:
- Fujitsu’s new technologies dramatically cut the costs of creating AI solutions for visual inspection applications, including manufacturing, infrastructure maintenance and healthcare
- The innovative solution combines advanced automatic unsupervised defect detection (typically 80-90% automatic discovery of regions of interest) with significantly faster AI-assisted dataset training and labelling (factor of 50 to 100x than previously achievable)
- Enables high quality labeled datasets to be created rapidly and cost-effectively, overcoming limitations associated with traditional deep learning methods
London, July 04, 2019
– Fujitsu Laboratories of Europe today announces two new technologies that significantly reduce the cost of AI solution creation for visual inspection applications. The novel solution uses a new type of defect detector that is trained on normal (non-defective) data, reducing dataset creation costs as well as enabling the detection of previously unseen patterns. This is combined with an AI-accelerated Graphical User Interface (GUI) that facilitates rapid cluster labelling based on automatically identified regions of interest, creating high quality training datasets. The combined result is highly accurate, automatic, unsupervised defect detection (discovering 80-90% of regions of interest automatically) with 50–100x faster dataset training and labelling.
Visual inspection is the principal method adopted analysing visual data, usually in the form of images, with the purpose of identifying regions of interest. It involves the painstaking analysis of large quantities of data in order to find a very small number of regions of interest. In manufacturing, this approach is used to identify defective products or defective areas in a product. In infrastructure maintenance applications, it is used to find cracks in bridges or holes in the road, while in healthcare it can be used to find patches of unhealthy tissue. By automating visual inspection, analysis time can be greatly reduced and a substantial cost overhead removed. In addition, it delivers more consistent results, as a result of reducing the variation in results caused by different human interpretations. With regard to creating high quality datasets, the challenge centres around the very small number of regions of interest, involving high costs to inspect the very high numbers of images required in order to train an accurate AI model. For example, 100,000 images would need to be inspected in order to create a dataset containing 100 defects (average defect rate of 0/1%), and 1 million in order to create a more reasonable dataset with 1,000 regions of interest. Fujitsu Laboratories of Europe’s combined AI solution overcomes both of these issues, enabling high quality labelled datasets to be created rapidly and cost-effectively.
Fujitsu Laboratories of Europe’s CEO Dr Adel Rouz explains the significance of the new technology breakthrough, “This is the latest in a long line of Fujitsu’s novel AI technologies, applying our advanced data analytics and machine learning expertise to address complex non-intrusive testing applications. Once provided with a high volume of low-cost and easily available defect-free samples, our new defect detector technology is able rapidly to work out what to look for automatically. This simplifies and accelerates the creation of machine learning solutions, as well as enabling the detection of previously unknown anomalies. Combined with our new AI-assisted GUI, LabelGear, we have engineered a powerful new visual inspection tool that can be applied to a wide variety of tasks, reducing costs, improving accuracy and accelerating the overall process.”
Potential applications include manufacturing, where cameras are placed at key points on a production line, continuously monitoring product quality and identifying any potential defects. In the steel industry for example, where a 2km long steel coil is produced every hour, some 70,000 images are used to capture the surface of a single coil and over 1 million during the course of a day. With Fujitsu’s automated unsupervised solution, 80-90% of the defects can be automatically identified and assigned appropriate labels, covering around 200 types of defects that need to be recognised. Other potential applications include infrastructure monitoring and healthcare, where the solution can be used to diagnose and screen for abnormalities, such as chest abnormalities (using X-ray scans). In the US alone, around 150 million such health checks are performed each year. Manually labelling the enormous volume of resultant images is prohibitively costly and time-consuming but becomes feasible with Fujitsu’s automated unsupervised visual inspection technologies.
About the Technologies
Fujitsu Laboratories of Europe’s solution uses predominantly defect-free data to create an accurate model of what is normal (e.g., good products, normal surface, healthy tissue). A comparison between the learned defect-free model and actual image highlights any unexpected patterns (regions of interest), irrespective of whether such patterns have been previously seen by the system. While the former data is very scarce, the latter is abundant, making the model considerably less costly to create. By using unlabelled data alone, the system can automatically discover 80-90% of the regions of interest.
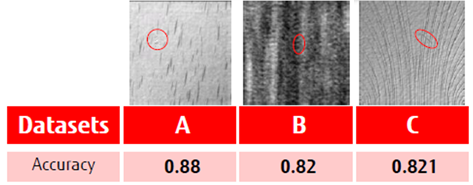 Figure 1: Accuracy obtained on 3 datasets from Manufacturing
Figure 1: Accuracy obtained on 3 datasets from Manufacturing
The AI-accelerated GUI, LabelGear allows labels to be rapidly assigned to the regions of interest that were automatically discovered in order to create a high-quality training dataset. It clusters regions of interest based on their visual appearance in order to allow the user to label entire clusters rather than single images at a time. Once a small subset of the data has been labelled (e.g. 10%), the GUI builds an internal representation of the data that allows it to predict the class of the data that is still unlabelled. This enables the GUI dynamically to reorder the target labels, consistently positioning the most likely matches on top, thereby reducing the time involved in finding the right label. By automatically identifying the regions of interest, labelling a cluster at a time and dynamically reordering the labels allows high-quality datasets to be created 50x–100x faster than with conventional technologies.
Depending on the required potential solution, Fujitsu’s two technologies can be used separately or together. The anomaly detection technology can be used directly to detect any type of deviation from what is considered as the norm. However, if the solution requires the type of deviation (or defect) to be specified, LabelGear can be used to assign the required labels.
For classification or detection tasks, if large quantities of unlabelled image data are available, LabelGear can be directly used to assign the needed labels rapidly. However, if the solution requires the flagging of anomalies not present in the training data-set, Fujitsu’s anomaly detection technology can provide this extra feature.
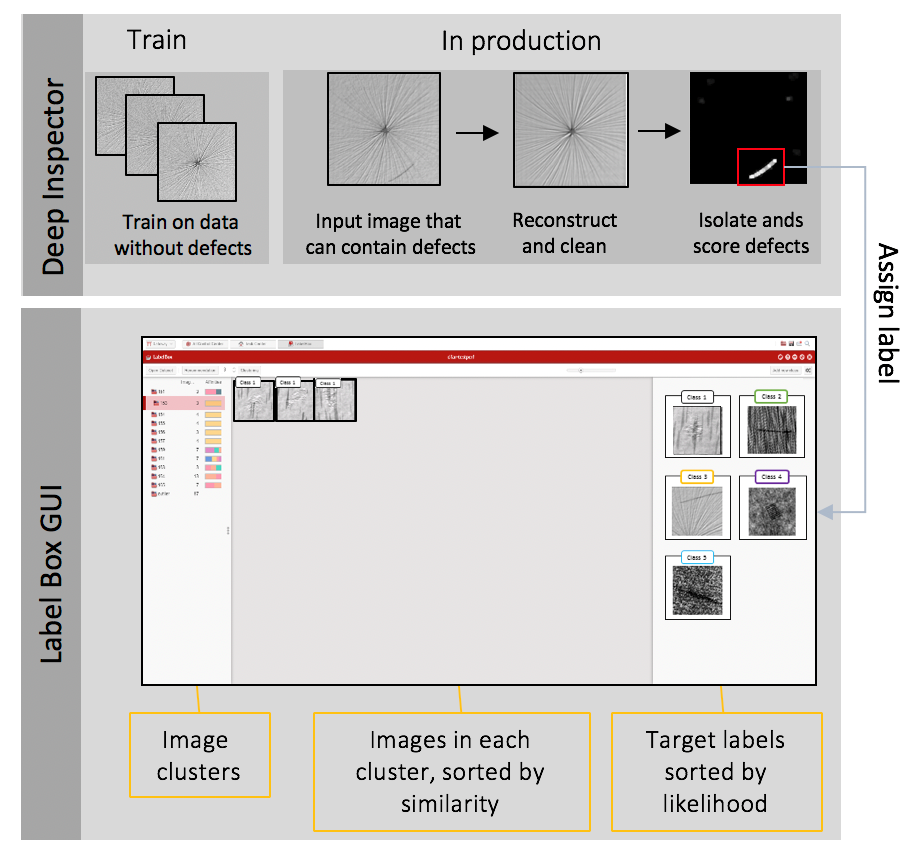 Figure 2: The two new technologies used to generate a high-quality labelled dataset. The first technology uses data without defects to automatically mark regions of interest. Labels are then assigned to these regions via LabelGearTM
Figure 2: The two new technologies used to generate a high-quality labelled dataset. The first technology uses data without defects to automatically mark regions of interest. Labels are then assigned to these regions via LabelGearTM
About Fujitsu
Fujitsu is the leading Japanese information and communication technology (ICT) company, offering a full range of technology products, solutions, and services. Approximately 132,000 Fujitsu people support customers in more than 100 countries. We use our experience and the power of ICT to shape the future of society with our customers. Fujitsu Limited (TSE: 6702) reported consolidated revenues of 4.0 trillion yen (US $36 billion) for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2019. For more information, please see http://www.fujitsu.com.
About Fujitsu Laboratories of Europe
Established in 2001 and with an active presence in Europe since 1990, Fujitsu Laboratories of Europe Limited represents Fujitsu Laboratories across EMEIA, focused on the creation of cutting-edge innovations that benefit society and business. By adopting a co-creation strategy and working with customers and collaboration partners, its extensive R&D and co-creation activities span Artificial Intelligence, Trusted Technologies, AI Ethics, Blockchain, Cyber Security, Approximate Computing and Digital Annealer applications. Fujitsu Laboratories of Europe is considered one of the leading research and development centers in EMEIA, with its wide range of R&D and co-creation activities focusing on cutting edge innovations that address real-world challenges, underpinned by ethical concepts. For more information, please see http://www.fujitsu.com/uk/fle/.
Media Contacts
Georgina Garrett
Director
Garrett Axford Ltd (on behalf of Fujitsu Laboratories of Europe Ltd)
 Phone: +44 7778 216004
Phone: +44 7778 216004
 E-mail: fujitsu@garrett-axford.co.uk
E-mail: fujitsu@garrett-axford.co.uk
All other company or product names mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. Information provided in this press release is accurate at time of publication and is subject to change without advance notice.
Date: 04 July, 2019
City: London


![]() Phone: +44 7778 216004
Phone: +44 7778 216004![]() E-mail: fujitsu@garrett-axford.co.uk
E-mail: fujitsu@garrett-axford.co.uk
 01235 797711
01235 797711
