Kawasaki, Japan, August 02, 2019
Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. today announced that it has developed a technology that can compare biometric information while it is still encrypted, with the same accuracy and processing speed as conventional biometric authentication systems.
Conventional technologies have been developed that can authenticate encrypted biometric information, but there were issues with the comparison accuracy or in the processing speed. Now, Fujitsu Laboratories has developed a technology that uses palm vein authentication to prevent the degradation of comparison accuracy that occurs when encryption is applied, while increasing the speed of comparison processing.
Because this technology enables quick and accurate comparison of biometric information while it is constantly encrypted, it can create a payment system using safe and secure palm vein biometric authentication in environments such as a cloud environment via the internet.
Development Background
In recent years, the use of biometric authentication has become more common as a safe and convenient method of identifying a person. Fujitsu Laboratories early on developed palm vein authentication to meet the need for an authentication system that could identify a person with just biometric information, without using information such as a password or a card. In 2018, Fujitsu Laboratories announced a biometric authentication technology that combined facial recognition with palm vein authentication. Going forward, Fujitsu expects to see wider use of biometric authentication in a variety of situations, such as for payments when shopping, for logging in to websites and systems, and for accessing secure rooms.
Conventional biometric authentication systems could only operate in closed environments using dedicated connections. In the future, however, the implementation of biometric authentication systems operating in open environments via the internet is expected, as there will be more usage of cashless payment at large-scale chain stores
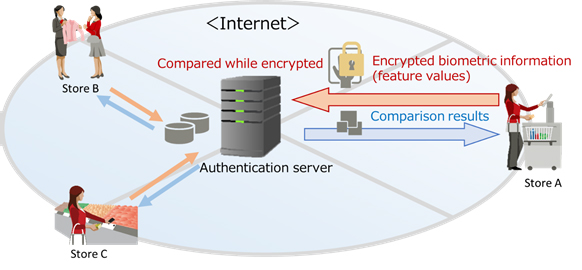 Figure 1: Usage scenario
Figure 1: Usage scenario
Issues
In order to realize large-scale and more secure biometric authentication in an open environment, the biometric information encrypted by a terminal must be sent to the authentication server and collated while it is encrypted. With conventional technologies that compared biometric information while it was still encrypted, in general, biometric image data is converted to a simple code (a string of numbers), and that is encrypted by multiplying it with a random number. Nonetheless, with existing technology, comparison accuracy deteriorated by converting the complex feature values of a biometric image to a simple code, while comparison processing took a long time when the code became very long. In other words, there were issues that had to be resolved before the technology could be commercialized.
About the Newly Developed Technology
Now, Fujitsu Laboratories has developed encrypted authentication technology for palm vein authentication that is capable of greater accuracy and speed. The features of this newly developed technology are as follows.
1. Mitigating the degradation of comparison accuracy
Biometric authentication compares the degree of similarity of feature values(1) in the registered biometric information with those of the biometric information input when a user tries to use the authentication system. Now, Fujitsu Laboratories has developed a technology that generates codes without compromising the comparison accuracy, as it dynamically adjusts the area size of the image that are converted into feature value codes, based on the degree of their impact on comparison results. This limits changes to the degree of similarity of the feature values due to conversion to a numerical code.
2. Dramatically shortening processing time
Because conventional code conversion technology generated a code from the data of the entire biometric image, comparison processing could be time-consuming. Now, Fujitsu Laboratories has developed a technology that can automatically select parts of the biometric image data to convert to code, choosing areas that have a significant impact on comparison accuracy. By mitigating the proliferation of codes, this technology delivers high speed authentication, on the same level as biometric authentication technologies that do not convert images to numerical codes.
Effects
When comparison accuracy using this newly developed technology was tested with the palm vein data of 10,000 hands, and compared with a method that did not convert the data to a numerical code, Fujitsu confirmed that the two technologies delivered more or less the same comparison accuracy and processing time. Moreover, the company combined Fujitsu Laboratories' feature code(2) generation technology announced in 2013, which can generate multiple feature codes from a single piece of biometric information. As a result, the new technology can utilize feature codes which vary with different biometric authentication services, leading to an effective countermeasure in the unlikely event of a data leak.
With this technology, it has become possible to safely use biometric authentication systems that previously required dedicated servers and dedicated networks, in an open environment. This brings into view a future where people can make payments with their bare hands, using a safe and secure biometric authentication system in a cloud environment.
Future Plans
Fujitsu Laboratories will continue to further increase the processing speed of the newly developed technology, with the goal of commercializing the technology during fiscal 2019.
Related Links
Fujitsu Develops Non-contact Biometric Integration Technology as an Optimal Solution for a Cashless Society (press release, October 4, 2018)
Fujitsu Develops World's First Authentication Technology to Extract and Match 2,048-bit Feature Codes from Palm Vein Images (press release, August 5, 2013)
![]() E-mail: biometric-encryption-2019@ml.labs.fujitsu.com
E-mail: biometric-encryption-2019@ml.labs.fujitsu.com
