- Table of Contents
What is e-seal? Review Again
According to Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications's e-seal Guidelines, an e-seal is a "A system to confirm that documents, etc. have not been tampered with since the measures were taken, such as encryption, etc., which is implemented for the purpose of indicating the organization, etc. of the issuer of electronic documents, etc." (*1). In other words, an e-seal on a digital document guarantees the legitimacy of the organization from which the data originates.
- At first glance, e-seal and electronic signature seem to have the same function. In both cases, it is possible to confirm that a document has not been tampered with by encrypting an electronic document. The difference is that an e-seal can prove the legitimacy of the issuing organization, while an electronic signature can indicate an individual's consent to the content of the document by the signer.
European countries are among the first to promote the use of e-seals to enhance the safety of digital documents. In Europe, for example, digitalization is being strategically pursued with the enactment of the eIDAS (eIDAS) regulations in 2016 with the aim of creating a "digital single market.". (*2)
- *1Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications "Guidelines for e-seals" issued on June 25, 2021
https://www.soumu.go.jp/main_content/000756907.pdf (in Japanese) - *2Digital Single Market: Integrating the digital markets within a domain into one and receiving equal benefits from people, goods, capital and services.
eIDAS (eIDAS) rules: Electronic Identification and Trust Services Regulation. A standard regulation that went into effect in 2016 with the aim of extending the electronic signature law throughout the EU.
Why e-seals Are Necessary?
In Japan as well, there is a movement to inform the world of the future direction of trust services, including e-seals, that support the foundation of data distribution. Most of all, COVID-19 has forced us to replace face-to-face paper exchanges with digital documents via email and services. As the number of face-to-face deliveries has decreased, the risk of impersonation and document fraud has increased, and the need for the widespread use of e-seals is increasing.
Fujitsu has also been implementing initiatives using its own trust technology for many years. Computer as a Service (CaaS) systematize, and Data e-TRUST is launched. CaaS is Fujitsu's new suite of services designed to help advance cutting-edge research and enhance corporate competitiveness by making advanced computing technology accessible to everyone. One of these services is Data e-TRUST, which aims to provide advanced information security. This system aims to promote DX in society through a safe and secure data distribution system that ensures the authenticity of transaction information. As part of this effort, we are implementing e-seals.
About e-seal which Fujitsu is working on. Demonstration conducted in cooperation with Teikoku Databank
Starting in April 2022, over a period of approximately 6 months, Fujitsu, in cooperation with TDB, conducted a demonstration test for the social implementation of the Japanese version of e-seal. And in November 2022, I wrote a series of articlesreportis published. (in Japanese)
purpose of the demonstration
This is to deepen understanding of whether e-seals can be used in actual business operations by actually using them, rather than on paper. The point is whether it is possible to verify the source of the data automatically, not by eye inspection. As a result of actual use, we will explore what kinds of problems exist in the automatic verification of the source of data and how we can solve them, and we will consider how we should be in business.
Outline of the demonstration experiment
By linking Fujitsu's Data e-TRUST, TDB's knowledge on corporate identity as an external certification organization, and Box, a content cloud provided by BOX Japan, we have developed a service model that utilizes e-seal. Using this environment, we confirmed the usefulness of e-seal by applying e-seal and performing verification operations when delivering digital documents using Box.
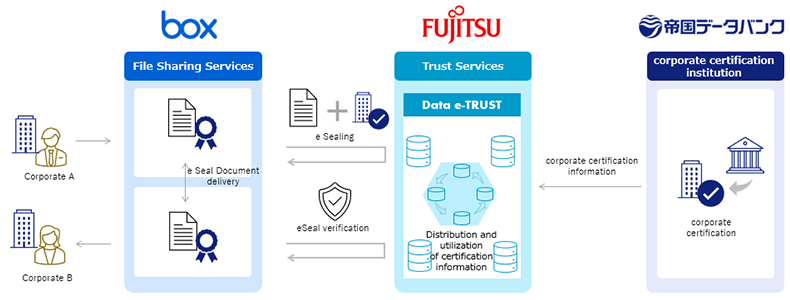 Service Model Image
Service Model Image
Process from e-seal issuance to verification
Issuance of certificate of step 1 "e-seal"
A corporation A who wants to use "e-seal" obtains a certificate for "e-seal" by "Data e-TRUST" linked with "Box" and "Trusted Corporation Account" issued by TDB after confirming the existence of the corporation in advance.
Step 2 Apply "e-seal"
When the corporation A who acquired the corporate account applies for "e-seal" to the digital document to be delivered by "Box", "e-seal" is given by "Data-e-TRUST" which is linked with "Box".
Step 3 Verify the "e-seal"
The corporation A delivers the document with the "e-seal" to the corporation B by using the "Box" in a different environment. "Data e-TRUST" and "e-seal" verify the source of the document.
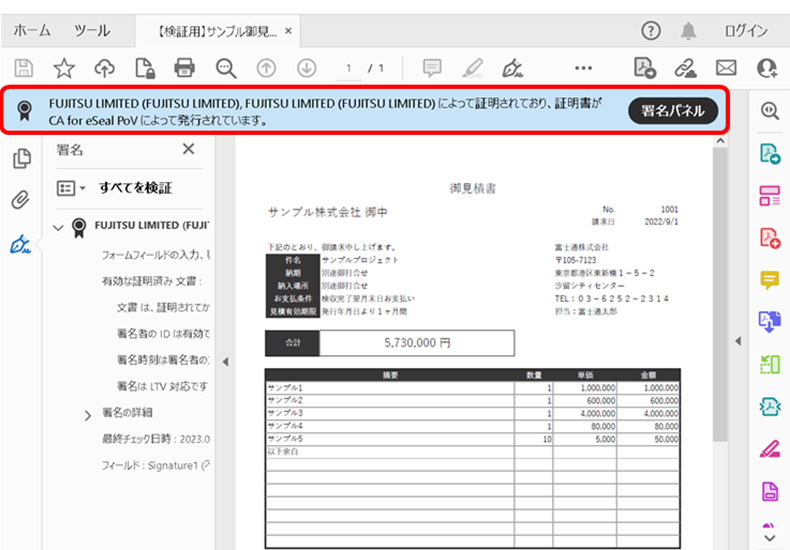 PDF files with e-seals (based on results of demonstration experiments)
PDF files with e-seals (based on results of demonstration experiments)
 Results of verifying the PDF file with e-seal on the box (from the results of the demonstration experiment)
Results of verifying the PDF file with e-seal on the box (from the results of the demonstration experiment)
Challenges and Prospects Presented by the Person in Charge After the Demonstration
TDB provided TDB with the means to ensure knowledge and authenticity of e-seals, and Fujitsu provided technology to attach e-seals to digital documents and a mechanism to link e-seals with services.
In fact, it is not that difficult to create a system that can be verified or attached with e-seals. Rather than building an e-seal system, I feel that there are challenges in standardizing the definition of e-seals, devising ways to make them easy to use in the world, and creating a framework for collaboration that can be easily used across various services. In order to resolve these issues in the future, we would like to resolve them in cooperation with our business partners with the following three points in mind.
- Usability: A user-friendly environment
- ID linkage: An environment in which users do not need to authenticate multiple times when using various services
- System linkage: An environment in which the service provider can easily link with the system without having to create a custom configuration
Currently, the e-seal system is being considered taking into account the culture of Japanese companies, but we are also considering interoperability with the European version that is ahead of us. TDB and Fujitsu aim to create user-friendly models that enable everyone to enjoy the convenience of digital documents.
Related Information
- report of the demonstration (in Japanese)
- [Press Releases] Fujitsu and Teikoku Databank to conduct joint trial of “Japanese electronic seal” to deliver verified digital documents between multiple companies
- [Teikoku Databank Press Release] Continued expansion of the "Japanese e-seal" social implementation demonstration with participating companies (in Japanese)
- [Press Releases] Fujitsu and Teikoku Databank release a report on the results of demonstration tests aimed at social implementation of the "Japanese e-seal." (in Japanese)
- Data e-TRUST