- Table of Contents
Technology Supporting the Expanding Metaverse
Metaverse is a coined word combining meta (transcendence) and universe (world), and refers to a three-dimensional virtual space constructed on the Internet.
In the metaverse, users can enjoy another world in the digital world by freely exploring the space and communicating with other users using their own avatars.
Although the metaverse has been utilized mainly in the field of games, it has recently expanded into other fields, such as virtual stores and offices that utilize the technology, and is attracting people’s attention.
The metaverse is a symbol of Web3 (a self-sovereign economics in a decentralized network). A technology called blockchain underlies Web3. You have probably heard of this word, which is used in the virtual currency (crypto assets) topic. Blockchain technology is “a type of database that uses cryptography to process and record transaction records in a decentralized manner by directly connecting terminals on a communication network.”*1 Compared to the conventional method where data is centrally managed on a server, data is distributed across multiple terminals, making it more difficult to falsify data and increasing its authenticity.
- *1
In addition, an important word in the metaverse is non-fungible token (NFT). NFT is a non-substitutable token (certificate of entitlement). By recording information about the owner and the data in the blockchain described above, it is difficult to falsify or misuse the data, and to give unique value. This allows, for example, the creation of one-of-a-kind items on the Internet or in games.
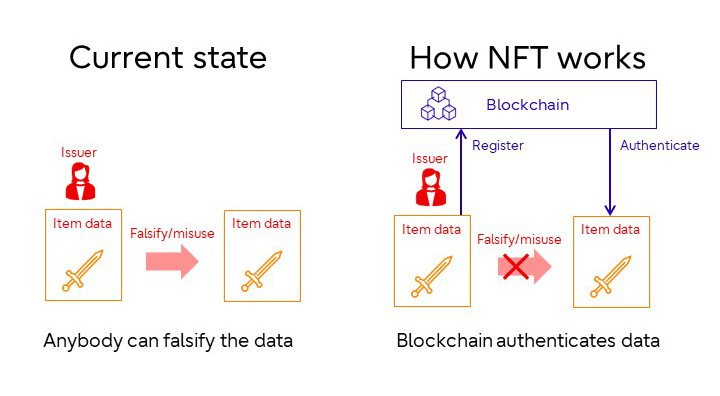 How NFT works
How NFT works
Three Companies Collaborate to Solve Issues Metaverse Faces
However, with the conventional NFT mechanism, which only registers the owner and data on the blockchain, there is still a risk of tampering and misuse, such as data being registered without permission by someone else pretending to be the owner.
Fujitsu is developing trust technology to guarantee the authenticity (trust) of digital signatures*2, such as who created the data and when and whether the data has been tampered with, in order to improve the convenience of digital signatures and promote their widespread use. One of these technologies is transparent trust-ensuring technology, which automatically detects user operations on files on cloud services and adds digital signatures to files automatically (transparently) without complex procedures. Furthermore, Fujitsu’s proprietary digital signature technology called Hash-chain based aggregate digital signature technology makes it possible to simultaneously guarantee the authenticity, order of signatures—not only the current data owner, but also the owners before and after that—and data non-tampering.
In the collaboration with JCB and JP GAMES, Hash-chain based aggregate digital signature technology was used for the data on the metaverse to realize a mechanism that cannot be tampered with or abused. This method is characterized by the fact that the data and the digital signature are integrated, preventing fraud and spoofing of the data. JCB will be responsible for proving the person (login/payment information) and JP GAMES will be responsible for proving the item data (guaranteeing that the item was created in the metaverse) to prevent data misuse in the metaverse.
The specific roles of each company are as follows:
| JCB | Utilization of accumulated solutions and knowledge as Japan's premier and leading international payment brand to provide settlement functions and trust information based on its settlement and ID authentication platforms; provision of a new service model for ensuring the reliability of transactions. |
|---|---|
| JP GAMES | Development of a multiverse*3 platform constructed with the PEGASUS WORLD KIT metaverse space construction technology framework and a passport that carries information about users who cross the border between real and virtual worlds in collaboration with JCB. |
| Fujitsu | Provision of hash-chain based aggregate digital signature technology that clarifies information concerning rights to digital data and virtual assets, as well as transparent trust-ensuring technology that can be linked to identity authentication infrastructure and services to streamline identity verification. |
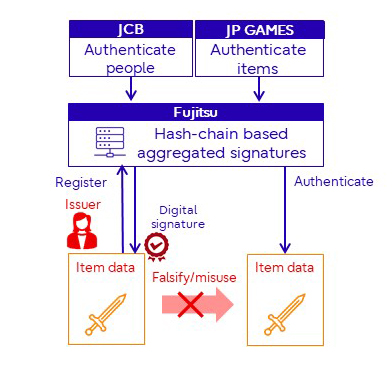 Expected roles of three companies
Expected roles of three companies
These technologies will help address the problem of children and elderly people accidentally selling or being defrauded of valuable data. For example, parental controls can be used to prevent a purchase agreement from being concluded without final approval by a parent or guardian. In addition, the system can easily add mechanisms to enhance the safety and security of services, such as working with payment companies and game operators to investigate fraud and disable problematic item data and trading records.
- Business model related to a rights management service, which enables the issuance and verification of digital signatures for digital data issued in the metaverse and game world.
- Technology that works in conjunction with the identity verification and payment functions provided by JCB to protect users from possible disadvantages in transactions.
- Implementation of a function that enables safe and secure use by minors and the elderly using Fujitsu’s proprietary digital signature technology, Hash-chain based aggregate digital signature technology.
- Ensure interoperability to allow future connections to existing NFT markets and other markets.
- *2Digital signature: A technology that applies public key cryptography to prove that the data sent by a user is authentic.
- *3Multiverse: A term coined by combining multi (multiple) and universe. The theoretical physics that there are multiple other worlds in parallel with the world you are in.
Thoughts of the person in charge on the project to solve social issues
We interviewed the person who successfully launched the three companies’ joint project, about his current state of mind and his thoughts for the future.

Hidenobu Oguri, Project Manager,
Trust as a Service Project, Data & Security Research Laboratory, Research Unit, Fujitsu Research
Transparent trust-ensuring technology, TaaS (Trust as a Service), was conceived as a technology to ensure trust in business processes in the COVID-19 pandemic. We have been discussing and conducting PoC with many people inside and outside the company to establish its use, and this press release is about its use as a technology to protect the safety and security of data rights management held by individuals and companies in the Web3 era. JCB and JP GAMES strongly agreed that there is a need for a data rights management solution that can be used safely by minors and the elderly with the increase in the number of metaverse and games using NFT and virtual currency. We will examine the various uses in the online world, which will continue to advance in the future.

Madoka Nitta, Social Business Development Division,
Digital Solution Business Unit, Fujitsu Limited
We have been discussing with JCB and JP GAMES on a safe, secure, and simple way to manage digital data rights on the metaverse, both for companies and for consumers, including children. Our laboratory technology TaaS came up to us. I am truly happy that we were able to encounter technologies and wonderful specialists with the potential to solve social issues and leverage the strengths of the three companies to launch the project in this way. We will continue the efforts of the three companies and keep you all posted on the positive results, so stay tuned!




