Archived content
NOTE: this is an archived page and the content is likely to be out of date.
Memory Mirror and Memory Patrol
Memory data protection by ECC and Extended ECC
Memory data is protected by ECC and Extended ECC.
ECC (Error Checking and Correction)
ECC is a data protection mechanism which recovers single bit errors by accurate detection and correction of corrupted data. It works by adding an ECC code to each data block.
Extended ECC (*1)
Extended ECC uses an ECC-like mechanism to rescue data left on faulty memory chips (DRAM).
*1: This corresponds to IBM's Chipkill function.
Memory Mirror provides memory redundancy
SPARC M10 incorporates a memory redundancy mechanism. Referred to as "Memory Mirror", it improves single system reliability using ECC to protect all data in memory, even from uncorrectable multi-bit errors. Memory Access Controllers equipped in processors help mirror memory chips.
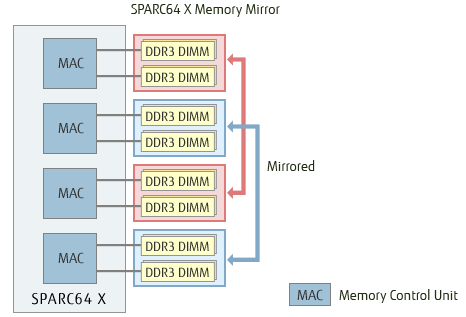
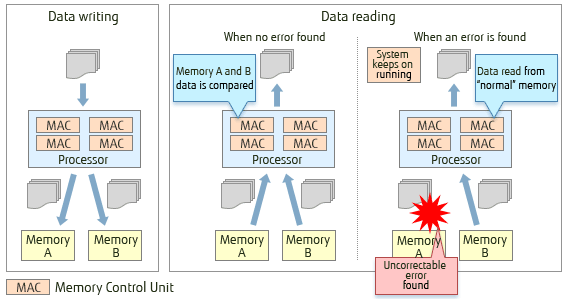
Memory Mirroring Actions
Data is written to both sides of the memory mirror at the same time (Memory A and Memory B).
As data is read its validity is checked using ECC. If no error is found the Memory Access Controller reconfirms data validity by comparing data in memory A and B. If an uncorrectable error is detected in memory A, data in memory B is used for the read operation, and vice versa.
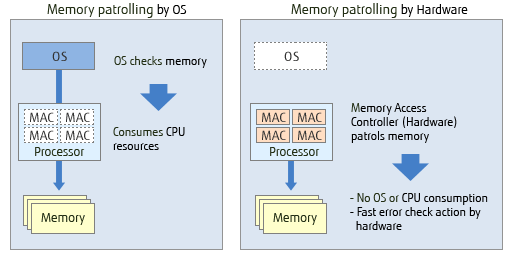
Memory Patrol fast and early error detection
A memory check function in hardware detects and corrects memory errors, downgrades memory and avoids OS or application failure caused by faulty memory chips (*2). This hardware function in the Memory Access Controller enables fast memory checking without consuming OS or CPU resources.
*2: Also referred to as “memory scrubber”




