Archived content
NOTE: this is an archived page and the content is likely to be out of date.
Fujitsu SPARC64 Timeline of Innovation

The development of Fujitsu SPARC64 processors began in the early 1990s. The first generation SPARC64 ran at just 118MHz, and 20 years later SPARC64 is now approaching 4GHz; more than 30x improvement in the clock frequency alone. Fujitsu continues to enhance the technical capabilities and performance of processors in Fujitsu mainframe computers, supercomputers, and UNIX servers. At Fujitsu, the processor design teams develop innovative processor technologies then apply those new technologies across Fujitsu platforms. Innovations with Fujitsu SPARC64 continue today with new processors in development.
November 2014 FUJITSU Supercomputer PRIMEHPC FX100
![]()


32 compute cores
2 assistant cores
Technology: 20nm
SPARC64 XIfx has 32 computing cores + 2 assistant cores, and has a theoretical compute performance of 1 TFLOP or higher. HPC-ACE2 (High Performance Computing – Arithmetic Computational Extensions 2), an enhanced version of the SPARC-V9 Instruction Set for HPC, was adopted for extended usability. The computational throughput was improved by employing two 256-bit wide SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) parallel execution units per processor core. Extremely high memory bandwidth was achieved by adopting the breakthrough HMC (Hybrid Memory Cube) technology, and the performance of internode communication bandwidth was improved through the low latency Tofu Interconnect 2. Parallel processing efficiency and overall job execution performance are greatly improved through the use of assistant cores for system interrupt handling, enabling compute cores to be dedicated for computing tasks.
April 2014 UNIX server Fujitsu M10
![]()


16 cores
Max. 3.7GHz
Technology: 28nm
This UNIX server processor is an enhanced version of the SPARC64 X with higher frequency, more Software on Chip features for greater application performance and transmission speed between CPUs increased up to 25Gbps (one-way).
SPARC64 X can be mixed with SPARC64 X+ within a Building Block of a Fujitsu M10-4S UNIX servers.
January 2013 UNIX server Fujitsu M10
![]()


16 cores
Max. 3.0GHz
Technology: 28nm
This UNIX server processor uses 28nm semiconductor technology. The number of cores, the capacity of Level 2 cache memory, and overall processor performance were dramatically improved over SPARC64 VII+. Software on Chip technology, derived from Fujitsu supercomputers, was first introduced in SPARC64 X executing common software functions directly on the hardware for significant performance benefits.
November 2011 FUJITSU Supercomputer PRIMEHPC FX10
![]()


16 cores
Max. 1.848GHz
Technology: 40nm
This HPC processor adopted 40nm semiconductor technology, and the number of cores was doubled from that of SPARC64 VIIIfx. Improved performance, without significant increases in power consumption, was achieved by increasing the number of cores.
September 2010 Supercomputer, the "K computer" (Note)
![]()


8 cores
2.0GHz
Technology: 45nm
The K supercomputer was jointly developed by RIKEN and Fujitsu and uses the SPARC64 VIIIfx processor. HPC-ACE (High Performance Computing-Arithmetic Computional Extensions), an enhanced architecture for the use in HPC, was adopted to achieve the world’s fastest performance achieving #1 rank in the TOP500 fastest computers of the world. High power efficiency was also achieved with a thorough power-saving design. A first for SPARC64 processors, memory controllers are embedded in the processor to greatly improve memory performance, system packaging and RAS.
December 2010 UNIX server SPARC Enterprise
![]()

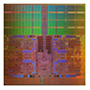
4 cores
Max. 3.0GHz
Technology: 65nm
This UNIX server processor is an enhanced version of the SPARC64 VII with higher frequency and twice the Level 2 cache memory capacity. SPARC64 VII+ is the first SPARC64 processor with a frequency of 3GHz or higher. This processor is compatible with SPARC64 VI and SPARC64 VII at the CPU module level and is used in SPARC Enterprise UNIX servers.
October 2009 UNIX server SPARC Enterprise
![]()


4 cores
Max. 2.88GHz
Technology: 65nm
This UNIX server processor is a higher frequency variant of the original SPARC64 VII processor.
November 2008 High-end technical computing server FX1
July 2008 UNIX server SPARC Enterprise
![]()


4 cores
Max. 2.52GHz
Technology: 65nm
Used in both UNIX and HPC servers, this processor increased the core count from 2 cores in SPARC64 VI to 4 cores. It also provided more advanced multi-threading capabilities by shrinking the semiconductor technology from 90nm to 65nm. The multi-thread control method was also improved from VMT (Vertical Multi-threading) to SMT (Simultaneous Multi-Threading) to further enhance throughput performance. This processor is compatible with SPARC64 VI at the CPU module level, and is used in SPARC Enterprise UNIX servers.
SPARC64 VII was also used in Fujitsu HPC servers, and improved HPC applications performance with a high-speed thread synchronization mechanism (hard barrier) and a double-speed mechanism for the CPU bus.
April 2007 UNIX server SPARC Enterprise
![]()


2 cores
Max. 2.4GHz
Technology: 90nm
This processor was developed by enhancing the SPARC64 V. It was used in SPARC Enterprise UNIX servers which were jointly developed by Fujitsu and Sun Microsystems.
A first for SPARC64, multi-core and multi-threading technologies were adopted and achieved significant improvement in throughput. VMT (Vertical Multi-Threading) was adopted as the multi-thread control method.
June 2004 UNIX server PRIMEPOWER
![]()
*Latter period


1 core
Max. 2.16GHz
Technology: 90nm
This processor was developed by improving the frequency of SPARC64 V. The size of the core area was reduced by adopting 90nm technology, leaving room for larger Level 2 cache memory capacity. With this second generation SPARC64 V processor, PRIMEPOWER became the first UNIX server in the world to run at 2GHz or higher.
October 2002 UNIX server PRIMEPOWER
![]()
*Early period
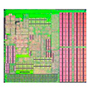
1 core
Max. 1.35GHz
Technology: 130nm
The origin of modern SPARC64 processors, this fifth generation SPARC64 processor was fully redesigned from the previous models and inherited high reliability technologies from Fujitsu mainframe processors, including instruction retry, complete correction of SRAM single bit errors, and a history function. Integration of Level 2 cache memory into the processor with 130nm semiconductor technology was first accomplished with this processor. The pipeline structure was renewed by adopting the basic structure for mainframe processors.
In order to improve compatibility with UltraSPARC-series processors of then Sun Microsystems, the JPS (Joint Programmer's Specification) was formulated by Fujitsu and Sun Microsystems. Instruction sets based on SPARC V9 and the JPS were adopted for SPARC64 V and later generations of SPARC64 processors.
August 2000 UNIX server PRIMEPOWER
![]()
*Latter period

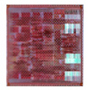
1 core
Max. 810MHz
Technology: 150nm
To increase frequency, this processor used 150nm semiconductor technology. In addition, the Level 1 cache size was doubled.
November 1998 UNIX server GP7000F
![]()
*Early period

1 core
Max. 330MHz
Technology: 250nm
The SPARC64 GP processor was the first server processor equipped with high-capacity external Level 2 cache. The processor featured support for installation in multi-processor systems, had redundant cache memory and bus interfaces, and was equipped with parity and ECC (Error Correction Code) methods for correcting 1-bit errors. Reliability was significantly higher than other UNIX processors of the time.
November 1996 S-Family Workstation
![]()
1 core
Max. 161MHz
Technology: 350nm
To increase frequency, this processor used 350nm semiconductor technology. As with the first generation SPARC64, multi-chip module technology was adopted, and cache memory and memory management units were mounted on a single board.
November 1995 S-Family Workstation
![]()

1 core
Max. 118MHz
Technology: 400nm
The first generation SPARC64 processor was the world's first 64-bit SPARC processor. It was developed by HAL Computer Systems, then a U.S. subsidiary of Fujitsu. The processor implemented an out-of-order execution method which was the most advanced and novel processor execution technology in the world at the time. With the first SPARC64 processor, the SPARC-V9 instruction set architecture was established. Enhancements over SPARC-V8 included 64-bit address space extensions, multi-processor support, and high reliability features.
(Note) "K computer" is a registered trademark of RIKEN.




