Archived content
NOTE: this is an archived page and the content is likely to be out of date.
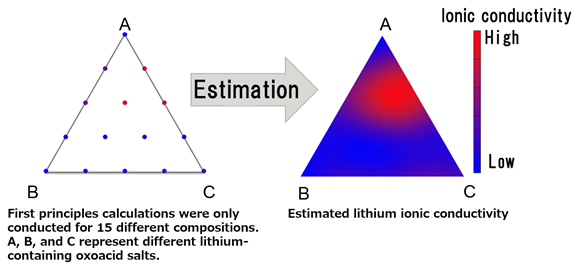
Fujitsu and RIKEN Demonstrate AI's Utility in Material Design
Improving the development of solid electrolytes with high ionic conductivity for use in all-solid-state lithium-ion rechargeable batteries
Fujitsu Limited,RIKEN
-
[1] RIKEN AIP-Fujitsu Collaboration Center
A collaboration center formed in April 2017 between the RIKEN Center for Advanced Intelligence Project (AIP) and Fujitsu Limited. The center undertakes joint research centered on the theme of creating AI that looks beyond the normal scope, which will support people in making good decisions based on accurate predictions of the future, even in the face of uncertain changes in the environment.
-
[2] First principles calculation
A materials simulation method. Using electronic structure theory, grounded in quantum mechanics, it is capable of calculating various characteristics of materials and substances just from the number and types of atoms in them, without using empirical parameters. However, it has an extremely significant computational load compared with other methods.
-
[3] Materials informatics
An effort to accelerate the search for new materials by combining and fusing technologies in the materials field, such as materials synthesis and analysis technologies and materials simulation, with such technologies as data science and AI. It is expected to significantly reduce the time and cost required for materials development.
-
[4] Bayesian inference method
A method for probabilistically inferring the causes of a phenomenon based on observed realities, which is based on the way of thinking underlying Bayesian probability.
-
[5] All-solid-state batteries
Batteries using a solid electrolyte in place of a liquid electrolyte. Ions move within the solid material. Because all materials in these batteries are solid, there is no danger of leaks or ignition. These batteries can be used in environments where existing batteries cannot be used, such as high temperature environments, and active development is ongoing for these batteries as next-generation batteries which can easily support higher voltages and capacities.
About RIKEN
RIKEN is Japan's largest research institute for basic and applied research. Over 2500 papers by RIKEN researchers are published every year in leading scientific and technology journals covering a broad spectrum of disciplines including physics, chemistry, biology, engineering, and medical science. RIKEN's research environment and strong emphasis on interdisciplinary collaboration and globalization has earned a worldwide reputation for scientific excellence.
Website: www.riken.jp/en/
Facebook: www.facebook.com/RIKEN.english
Twitter: @riken_en
About Fujitsu
Fujitsu is the leading Japanese information and communication technology (ICT) company offering a full range of technology products, solutions and services. Approximately 155,000 Fujitsu people support customers in more than 100 countries. We use our experience and the power of ICT to shape the future of society with our customers. Fujitsu Limited (TSE: 6702) reported consolidated revenues of 4.5 trillion yen (US$40 billion) for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017. For more information, please see http://www.fujitsu.com.
All company or product names mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. Information provided in this press release is accurate at time of publication and is subject to change without advance notice.
Date: 16 March, 2018
City: Tokyo and Wako, Japan
Company:
Fujitsu Limited ,RIKEN