Archived content
NOTE: this is an archived page and the content is likely to be out of date.
Fujitsu Deep Learning Technology Successfully Estimates Degree of Internal Damage to Bridge Infrastructure
Enables estimation of failure, state of degradation with surface-mounted sensors
Fujitsu Limited,Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd.
-
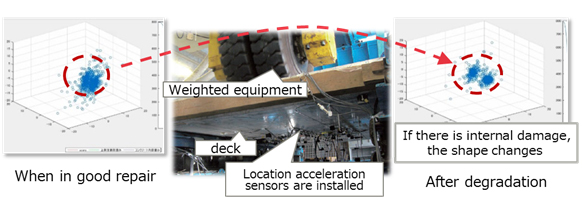
[1] Verification tests of fatigue degradation of bridges
This verification test was carried out by RAIMS, as part of a commissioned research project on the research and development of technology promoting the use of monitoring technology for societal infrastructure, commissioned by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism as part of the Cabinet Office’s Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP), promoting technology to manage, update, and maintain infrastructure. Summary of the verification tests conducted by RAIMS Goal: Evaluate technology for monitoring the fatigue degradation of bridges Testing period: July-August 2015 Testing summary: Acceleration test to recreate the process of fatigue degradation of bridge decks in simulation, using an actual-size bridge deck and heavy load equipment (weighted wheeled testing apparatus). For the test, strain sensors were embedded within the actual-size bridge deck. In addition, the vibration data that was used for analysis was collected via acceleration sensors attached to the surface of the bridge deck. Location: Yamaguchi University
-
[2] Research Association for Infrastructure Monitoring System (RAIMS)
An organization consisting of 14 companies and legal entities, with the goal of promoting the rapid commercialization of monitoring technology. Fujitsu also carries out research and development as a member of the association.
-
[3] Bridge deck
The floor or surface of the bridge, which transfers the weight of vehicles travelling over the bridge to the columns or girders supporting the bridge.
-
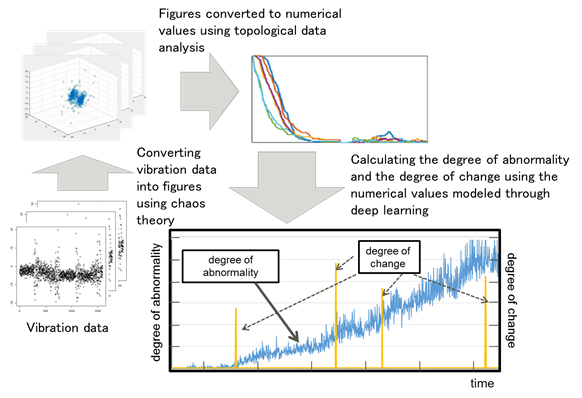
[4] Deep learning technology for time-series data
Proprietary technology from Fujitsu Laboratories that accurately analyzes time-series data using a data analysis method called topological data analysis. “Fujitsu Develops New Deep Learning Technology to Analyze Time-Series Data with High Precision” (press release, February 16, 2016: http://www.fujitsu.com/global/about/resources/news/press-releases/2016/0216-01.html)
-
[5] Estimation of the degree of damage
During the acceleration tests, the degree of damage to the experimental bridge deck was judged visually by engineers in accordance with the Japanese Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism’s guidelines for the periodic inspection of bridges, and estimated according to these results, as well as the results of an AI-based analysis.
About Fujitsu
Fujitsu is the leading Japanese information and communication technology (ICT) company offering a full range of technology products, solutions and services. Approximately 155,000 Fujitsu people support customers in more than 100 countries. We use our experience and the power of ICT to shape the future of society with our customers. Fujitsu Limited (TSE: 6702) reported consolidated revenues of 4.5 trillion yen (US$40 billion) for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017. For more information, please see http://www.fujitsu.com.
About Fujitsu Laboratories
Founded in 1968 as a wholly owned subsidiary of Fujitsu Limited, Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. is one of the premier research centers in the world. With a global network of laboratories in Japan, China, the United States and Europe, the organization conducts a wide range of basic and applied research in the areas of Next-generation Services, Computer Servers, Networks, Electronic Devices and Advanced Materials. For more information, please see: http://www.fujitsu.com/jp/group/labs/en/.
All company or product names mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. Information provided in this press release is accurate at time of publication and is subject to change without advance notice.
Date: 28 August, 2017
City: Tokyo and Kawasaki, Japan
Company:
Fujitsu Limited ,Fujitsu Laboratories Limited