Archived content
NOTE: this is an archived page and the content is likely to be out of date.
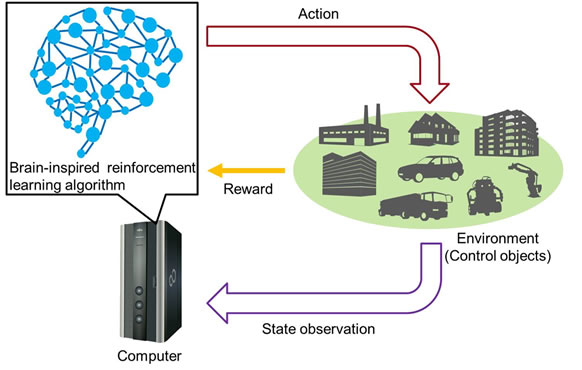
Fujitsu and OIST Begin Joint R&D on Reinforcement Learning Algorithms Utilizing Neuroscience Insights
In pursuit of AI with human-like applied skills
Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST),Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd.
About OIST
Established in November 2011, Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) is an interdisciplinary graduate school offering a 5-year PhD program in Science. Its mission is to provide internationally outstanding education and research in science and technology, thus contributing to the sustainable development of Okinawa. More than 400 researchers from over 50 countries are conducting their research in Neuroscience, Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology, Environmental and Ecological Science, Mathematical and Computational Science, Physics and Chemistry.
About Fujitsu
Fujitsu is the leading Japanese information and communication technology (ICT) company, offering a full range of technology products, solutions, and services. Approximately 156,000 Fujitsu people support customers in more than 100 countries. We use our experience and the power of ICT to shape the future of society with our customers. Fujitsu Limited (TSE: 6702) reported consolidated revenues of 4.7 trillion yen (US$41 billion) for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016. For more information, please see http://www.fujitsu.com.
About Fujitsu Laboratories
Founded in 1968 as a wholly owned subsidiary of Fujitsu Limited, Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. is one of the premier research centers in the world. With a global network of laboratories in Japan, China, the United States and Europe, the organization conducts a wide range of basic and applied research in the areas of Next-generation Services, Computer Servers, Networks, Electronic Devices and Advanced Materials. For more information, please see: http://www.fujitsu.com/jp/group/labs/en/.
Press Contacts
![]() E-mail: media@oist.jp
E-mail: media@oist.jp
Company:Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST)
Technical Contacts
Knowledge Information Processing Laboratory
![]() E-mail: bsrl@ml.labs.fujitsu.com
E-mail: bsrl@ml.labs.fujitsu.com
Company:Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd.
All company or product names mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. Information provided in this press release is accurate at time of publication and is subject to change without advance notice.
Date: 12 October, 2016
City: Onna and Kawasaki, Japan
Company:
Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) / Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd.