Kawasaki, Japan, November 11, 2014
Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. today announced that it has developed the world's first technology to optimize the allocation of wireless base stations for LTE-Advanced(1). This design technology determines the ideal placement of base stations through simulations to ensure a smooth communications environment for users.
Data traffic now makes up the bulk of mobile communications, creating a need for design methods that can allocate base stations for optimal communications speeds. But with coordinated multi-point (CoMP) transmission(2), which is expected to be a part of the emerging communications standard LTE-Advanced, there is no confirmed method for rapidly calculating the user's communications speed, which is a barrier to designing base station allocation for LTE-Advanced. Fujitsu Laboratories has now developed an algorithm that can rapidly calculate user communications speeds, even with CoMP.
When base stations are allocated using this technology, the same communications speeds can be attained as with other methods, but with 30% fewer base stations, while resolving connection difficulties in mobile communications.
Details of this technology are being presented at SmartCom 2014, opening October 30 in Singapore.
Background
With mobile traffic increasing every year, mobile communications systems need more capacity. One way that system capacity is increased in the emerging mobile-communications standard, LTE-Advanced, is through the use of macrocells, where a single base station covers a large area, together with small cells, where a single base station covers a limited area. The ability to design base station allocation in such a way that optimizes placement is important when installing compact base stations for small cells.
Technological Issues
Data communications, including email, web access, and streaming media, now account for the bulk of mobile traffic. Given this, when designing the layout of base stations for data communications, it is important to optimize user communications speeds, to improve the perception of communications speed among users, as well as to make it easier to connect. Accordingly, there have been efforts underway to develop algorithms to rapidly calculate user communications speeds. The coordinated multi-point transmissions in the emerging standard LTE-Advanced allow for a handset to receive the same signal from both a macrocell and small cell, which can avoid inter-cell interference.
In existing methods, each base station is assumed to have a unique set of users allocated to it through a process called scheduling, and user allocation rates have been calculated using a fast-calculation algorithm(3). But because this method is incompatible with coordinated multi-point transmissions, it cannot be used to correctly calculate user allocation rates, leaving no way to determine the ideal placement of base stations that use CoMP (Figure 1).
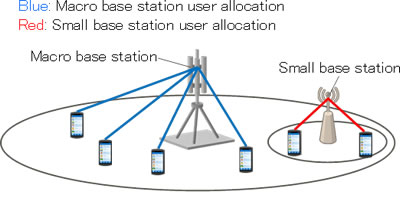 Figure 1: Designing base station allocation using existing fast-calculation techniques
Figure 1: Designing base station allocation using existing fast-calculation techniques
About the Technology
Fujitsu Laboratories has now developed a design technology for allocating base stations that can correctly calculate user allocation rates while taking into account CoMP (Figure 2). In this technique, newly introduced conditions make it possible to rapidly calculate user allocation rates when using CoMP, which in turn makes it possible to determine the optimal placement of base stations with CoMP functionality.
The design process for allocating base stations is as follows.
- Add a base station.
- Calculate user allocation rate assuming CoMP (fast-calculation algorithm).
- Calculate user communications speeds based on user allocation rate and received signal quality.
- Determine establishment of base station.
In this new method, the total user allocation rate in transmissions using CoMP, shown in green in Figure 2, and represented by the term α, and the total user allocation rates in uncoordinated transmissions, shown in blue and red, and represented by the term 1-α, are used in a fast-calculation algorithm, which can accurately calculate each user allocation rate. This can be used to obtain each user's communications speeds based on user allocation rates and received signal quality, and those totals can be used to determine allocation for base stations.
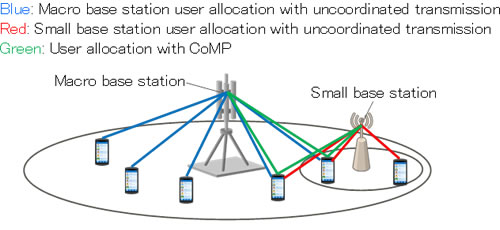 Figure 2: Designing base-station allocation with support for coordinated multi-point transmission
Figure 2: Designing base-station allocation with support for coordinated multi-point transmission
Results
This technology makes it possible to calculate optimal allocation for LTE-Advanced base stations, and can be expected to dramatically increase communications quality when adding base stations (Figure 3). The result is that a given level of communications capacity can be ensured while adding 30% fewer base stations than would otherwise be needed, while at the same time resolving connection difficulties for mobile communications and providing a smooth communications environment to users.
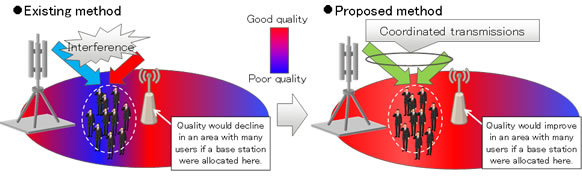 Figure 3: Results of this technology
Figure 3: Results of this technology
Larger View (64 KB)
Future Plans
Fujitsu Laboratories is continuing to study ways to optimize base station allocation, with the goal of a practical implementation around 2016. The company plans to continue adapting this technique to new features of LTE-Advanced and its successor communications standard, 5G(4).
![]() E-mail: press_scm14@ml.labs.fujitsu.com
E-mail: press_scm14@ml.labs.fujitsu.com

