Archived content
NOTE: this is an archived page and the content is likely to be out of date.
Fujitsu Laboratories Develops Fast Recovery Process for Multiple Disk Failures
Cuts recovery time by more than 20% from existing methods, reducing risk of digital media data loss
Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd.
Kawasaki, Japan, October 06, 2014
Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. today announced the development of a disk-recovery technique that is faster than existing methods and that can handle multiple failures, reducing the risk that important data will be lost.
RAID(1) is a widely used technology for protecting data against disk failures, but with the explosive growth in data being generated through the use of web services, the increase in time needed to recover data lost through disk failures is becoming a problem.
Fujitsu Laboratories has now developed a high-speed recovery process, devising a unique structure for managing blocks of data - units of storage - by groups, which maintains the same tolerance to disk failures as the existing RAID technology while speeding up recoveries by 20% or more with flexible trade-off of space efficiency in accordance with the usage scenario when there are multiple failures, such as when two disks fail simultaneously.
The development of this process will enable faster recovery of storage as online content increases in line with an expansion in cloud and web services.
Details of this technology have been announced at USENIX HotDep '14, opened October 5 in Colorado.
Background
In recent years, digital media data, which plays a central role in web services, has been experiencing an explosive rate of growth, exceeding 70% per year. The crucial importance of data to these services means that a number of measures are used to guard against digital media data loss, including triple-redundant copies, but the sheer volume of data means that the cost of storage cannot be ignored. Triple-redundant storage means triple the storage requirements; to use storage capacity more efficiently, in recent years RAID technology, long established as a method of protecting companies' mission-critical data, has been receiving renewed attention. Rather than storing complete copies of each piece of data, introducing "parity" - redundant pieces of data that summarize other data as part of a protection system - allows for the same degree of protection as triple-redundancy but with significantly less actual redundancy (Figure 1).
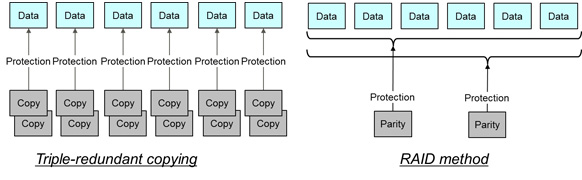 Figure 1: Switching from triple redundancy to RAID improves capacity utilization
Figure 1: Switching from triple redundancy to RAID improves capacity utilization
Issues
In standard RAID implementations, such as the widely used RAID 5 and RAID 6, all the parity is used to protect all the data. If a given disk fails, it is necessary that together with the parity that protects each piece of data stored on the failed disk, the remaining data be used to reconstruct the lost data. This means a lengthy recovery process and an increased risk that additional data will be lost during the recovery process itself (Figure 2). For example, when using 48 disks, each with 4-TB capacity and 15 Mbps random I/O performance, recovering from simultaneous failures of two disks is calculated to take more than 10 hours.
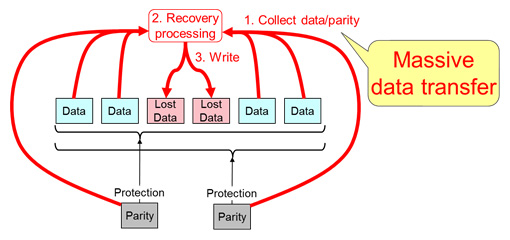 Figure 2: In conventional RAIDs, data recovery involves massive data transfers
Figure 2: In conventional RAIDs, data recovery involves massive data transfers
About the Newly Developed Technology
Fujitsu Laboratories has developed a method to quickly recover data while maintaining the same levels of reliability as RAID technology.
Features of the new technology are as follows.
- Multilayered parity-protection reduces data recovery processing volume
The range of protection offered by each parity does not cover all of the data, but rather is limited to a portion of the data. Additionally, Fujitsu Laboratories developed a unique approach using a partially overlapping range of parity protection (Figure 3) to protect any of the pieces of data from loss. When a disk fails, only the minimum combination of parity and data needed for recovery is used, which shortens recovery time.
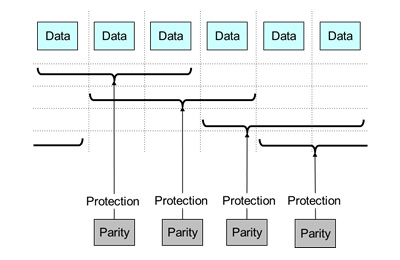 Figure 3: Range of multilayered parity protection
Figure 3: Range of multilayered parity protection
Data and parity are distributed over the different disks that make up a storage system. When a disk fails, recovery is performed by selecting the parity with the minimum amount of processing to recover the lost data that had been stored on that disk (Figure 4).
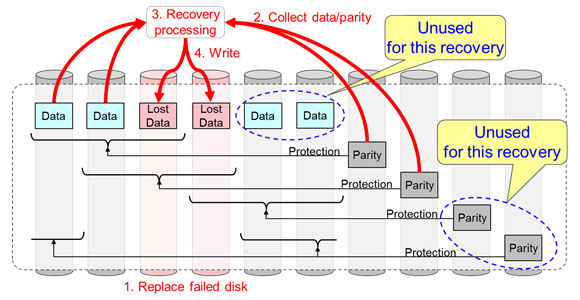 Figure 4: Accelerated recovery of lost data when disk fails
Figure 4: Accelerated recovery of lost data when disk fails
For example, in a comparative test for recovery of up to two simultaneously failed disks using the above mentioned 48 disks, each with a 4-TB capacity, when the protected range of parity is configured as described in Figure 4, the results confirmed that it was possible to shorten recovery time by over 20% compared to current RAID technology.
- The structure for the parity protection range can flexibly change with usage contexts
With the multilayered, overlapping structure of parity-protection range, there are mutual tradeoffs between recovery time (dependent on the minimum data-processing volume needed to restore data), probability of data loss (dependent on the number of parities that protect each piece of data), and capacity utilization efficiency (dependent on the ratio between data and parity). The range of parity protection can be tuned to provide the best balance given the importance of the data being stored.
Results
The use of this technology accelerates the recovery of data when a disk fails, even in the face of the explosive growth in stored data volume. This can be used to speed up recovery from storage devices with burgeoning content from cloud services and web services.
Future Plans
Fujitsu Laboratories plans to continue making improvements to this content-recovery technology with the goal of a practical implementation during fiscal 2015.
About Fujitsu
Fujitsu is the leading Japanese information and communication technology (ICT) company offering a full range of technology products, solutions and services. Approximately 162,000 Fujitsu people support customers in more than 100 countries. We use our experience and the power of ICT to shape the future of society with our customers. Fujitsu Limited (TSE: 6702) reported consolidated revenues of 4.8 trillion yen (US$46 billion) for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2014. For more information, please see http://www.fujitsu.com.
About Fujitsu Laboratories
Founded in 1968 as a wholly owned subsidiary of Fujitsu Limited, Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. is one of the premier research centers in the world. With a global network of laboratories in Japan, China, the United States and Europe, the organization conducts a wide range of basic and applied research in the areas of Next-generation Services, Computer Servers, Networks, Electronic Devices and Advanced Materials. For more information, please see: http://jp.fujitsu.com/labs/en.
Press Contacts
Public and Investor Relations Division
Inquiries
Company:Fujitsu Limited
All company or product names mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. Information provided in this press release is accurate at time of publication and is subject to change without advance notice.
Date: 06 October, 2014
City: Kawasaki, Japan
Company:
Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd.



