Archived content
NOTE: this is an archived page and the content is likely to be out of date.
Fujitsu and Nagoya University Develop Technology Enabling High-Speed Detection of Toxic Proteins Using DNA Aptamers
Detects toxins 100 times faster than before, holds promise for a future free of food poisoning
Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd.,Nagoya University
-
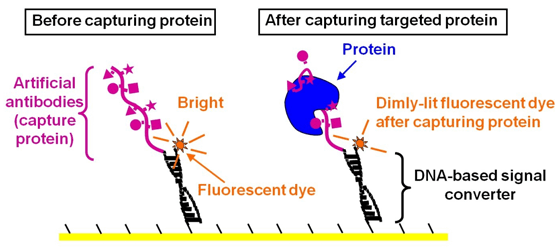
[1] Toxic proteins
As bacteria proliferates in food, the bacteria produces toxic proteins, leading to food poisoning. At times, the pathogenic bacteria itself causes food poisoning, while in other cases food poisoning can be attributable to toxic proteins produced by pathogenic bacteria. Toxic proteins account for approximately 10% of all causes of food poisoning. (Toxic proteins were the cause of a major food poisoning incident involving dairy products that occurred in Japan in 2000, which affected approximately 14,000 individuals. The toxic proteins that caused the food poisoning were attributable to enterotoxins produced by staphylococcus aureus. With the new technology referenced herein, Fujitsu and Nagoya University were able to detect enterotoxins).
-
[2] Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) of Japan
Partial development conducted from fiscal 2006 - 2009 (April 2006 - March 2010) as part of the project Formation of Innovation Center for Fusion of Advanced Technologies. An innovative research center for preventive medical engineering was established, in addition to the establishment of a R&D lab for international collaboration between industry and academia to promote cross-fertilization of research between nanobiotechnology - based on partnerships between medicine and engineering - and medical data processing.
-
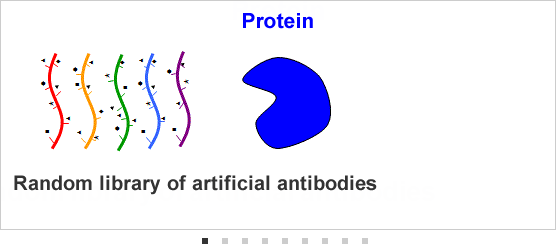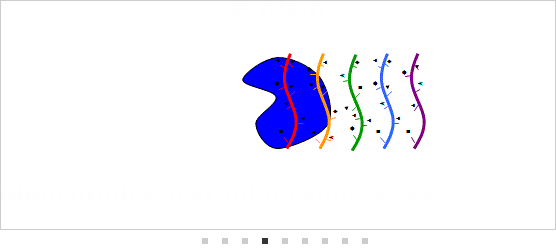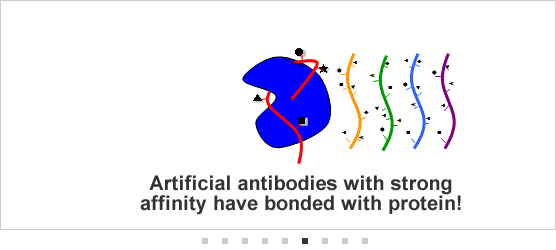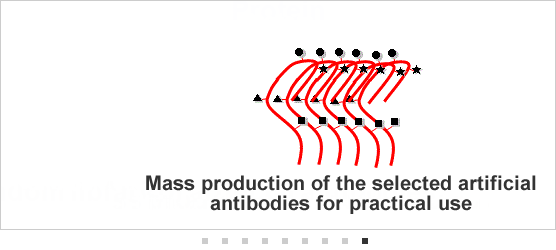
[3] Developing artificial antibody technologies for DNA material chemically modified to feature characteristics resembling amino acids (DNA aptamers) DNA stands for
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. (Chemically-synthesized DNA was employed in Fujitsu and Nagoya University's new technologies referenced herein). Part of Fujitsu's development of technologies for synthetic antibodies has been conducted under the Project for Developing Biotechnology IT Integration Equipment, of the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) of Japan.
-
[4] Conventional biochemical testing methods
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method and Western-blot (protein immunoblot) method.
-
[5] Walter Schottky Institute at the Technische Universität München
An institute within the Technische Universität München, which focuses on applied research for semiconductor electronics physics. In recent years, in view of international trends, the Institute is also active in interdisciplinary research.
-
[6] New research laboratory in Singapore
Official name: FUJITSU ASIA PTE LTD. Fujitsu Laboratories and R&D Division.
About Fujitsu Laboratories
Founded in 1968 as a wholly owned subsidiary of Fujitsu Limited, Fujitsu Laboratories Limited is one of the premier research centers in the world. With a global network of laboratories in Japan, China, the United States and Europe, the organization conducts a wide range of basic and applied research in the areas of Next-generation Services, Computer Servers, Networks, Electronic Devices and Advanced Materials. For more information, please see: http://jp.fujitsu.com/labs/en.
About Nagoya University
Nagoya University (NU) was first founded in 1871 as a temporary hospital and medical school. After undergoing several transitions, NU was established as an imperial university in 1939, and it has grown to be one of the world's top research universities. Throughout its history, NU has maintained a free and vibrant academic culture. Conducting research and education on all aspects of human beings, society, and nature, the University pursues its goal of contributing to the well-being and happiness of humankind. Nagoya University's fundamental objective is to cultivate leaders with genuine courage and intellect. We call such leaders "Yuuki-aru Chishiki-jin" , that is individuals who are able to harness their courage, curiosity, and creativity to fully, yet responsibly, exploit their freedom with their educational and research endeavors. Its multi-disciplinary curriculum is designed to cultivate ethical leaders who are able to develop innovative solutions, through inquiry and analysis, with strong communication and teamwork skills to be productive members of the global environment. Nagoya University welcomes highly motivated students who share this vision to apply to our programs. For more information: http://www.nagoya-u.ac.jp/en/
Technical Contacts
Business Incubation Planning Office
![]() E-mail: aptamer@ml.labs.fujitsu.com
E-mail: aptamer@ml.labs.fujitsu.com
Company:Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd.
Technical Contacts
Yasuko YoshidaSpecially Appointed Professor
Innovative Research Center for Preventive Medical Engineering
![]() Phone: +81(52)747-6377
Phone: +81(52)747-6377
Fax: +81(52)789-5499
Company:Nagoya University
All other company or product names mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. Information provided in this press release is accurate at time of publication and is subject to change without advance notice.
This press release has been revised as of December 17, 2018.
Date: 02 August, 2010
City: Kawasaki and Nagoya, Japan
Company:
Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd.,
Nagoya University,
,
,
,