Kawasaki, Japan, and Beijing, China, May 20, 2013
Fujitsu Laboratories Limited and Fujitsu Research and Development Center Co., Ltd. of China today announced the development of 3D hand gesture recognition technology that, using video captured on a single PC or tablet camera, can detect not only vertical and horizontal hand motion, but also the forward and backward movements of increasing or decreasing distance of a hand from the display.
With existing hand gesture recognition technology it has been possible to detect hand motions along the vertical and horizontal axes, which represent operations similar to moving a mouse cursor. However, detecting forward and backward hand motions—changing distance to perform the same function as a mouse click—has proven difficult. Fujitsu Laboratories and Fujitsu R&D Center have developed technology for accurately and quickly detecting the area of a hand based on models of palms, as well as a technology that detects forward and backward hand motions. This has made it possible for users to perform click operations through intuitive "push" gestures.
The new technology makes it possible to use hand gestures to perform a host of complex operations. For instance, a user can wave his or her hand up and down to make a menu selection on a PC and then confirm the selection with a "push" gesture, even from a distance. Maps and other images can also be expanded or shrunk with "push" and "pull" gestures.
Details of the new technology will be announced at the International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA) 2013, to be held starting May 20 at Ritsumeikan University in Kyoto, Japan.
Development Background
In recent years, attention has been gathering around hand gesture recognition technologies, which enable devices to be controlled through natural human movements. This approach to operating a device through hand motions that are detected with a camera is typically employed in situations when a user is physically separated from a PC or tablet device, when the user's hands are wet or dirty, or when the user does not want to directly touch a publically accessible device due to hygiene concerns. When attempting to substitute hand gestures for mouse operations, it has been possible to detect vertical and horizontal hand motions that are similar to how a mouse cursor moves, but detecting depth, as in forward and backward hand motions, which are equivalent to mouse clicks, has been difficult.
Technological Issues
Detecting forward and backward hand motions with a single camera relies on changes in the area of the user's palm. When the user is wearing short-sleeved clothing, however, or when the background is a color similar to the user's skin tone, it is difficult to distinguish between the user's palm and the background. As a result, it has been impossible to accurately extract the area of the user's hand from the background. Until now, methods using distance sensors that measure distance or multiple cameras have been used to detect forward and backward motion, but the equipment required for these approaches has made them quite costly.
About the New Technology
Fujitsu Laboratories and Fujitsu R&D Center have developed technology that can accurately extract the area of the user's hand from video captured on a single camera, thereby enabling constantly changing differences in the user's hand size to be reliably tracked. Key features of the new technology are as follows.
1. Hand area detection technology based on palm models
The hand is initially detected in a captured image, from which it is clipped out using block units of set sizes. Calculations are then made to determine whether or not the hand's characteristics (a palm model) exist as pre-registered data. The actual position and size of the hand is determined by performing this operation against the backdrop of the overall image while changing the position and size of the blocks. Next, the hand's area is extracted by taking the determined hand position and size and simultaneously changing the color threshold of certain parts to express the hand's original image. These operations ensure stable detection of the hand area.

Figure 1: Comparison with Conventional Methods
2. Depth detection technology based on changes in hand size
This technology is able to accurately estimate depth based on the continuity of the user's hand motions, including constantly changing features such as hand size, angle and central location. This allows "push" and "pull" motions to be detected with roughly 90% accuracy.
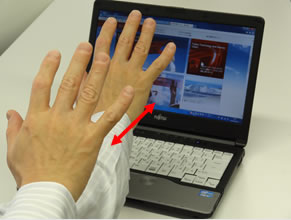
Figure 2: An operation that makes use of depth due to this technology
Results
There are many possible uses for this newly developed technology. For instance, a user can wave his or her hand up and down to make a menu selection on a device and then confirm the selection with a "push" gesture. Movies, music, sports, and other kinds of content can be selected by waving a hand left and right, and then confirmed with a "push" gesture. Maps and other images can also be expanded or shrunk with a "push" or "pull," thereby making possible even more complex operations via hand gestures. In addition, since motion can be detected with a single camera, equipment can be produced at a low cost.

Figure 3: Example Usage Scenarios
Future Development
With the aim of commercialization in fiscal 2014, Fujitsu Laboratories plans to evaluate the technology's usability while working to improve the accuracy of the hand detection and recognition technology.
![]() E-mail: depth-gesture@ml.labs.fujitsu.com
E-mail: depth-gesture@ml.labs.fujitsu.com

