Beijing, China, February 21, 2017
Fujitsu R&D Center Co., Ltd.[1] today announced an advanced deep learning technique for Chinese ancient character recognition. By applying the developed technique, highly accurate character recognition can be achieved with only a small number of training data. The technique consists of two types of recognition engines, one for supervised learning of character image features with their corresponding character labels, the other for analyzing a pair of images judging whether they are from the same character or not. Comparing with conventional supervised learning techniques, it can achieve high accuracy with a reduced number of training data. In a recent research for ancient Chinese character recognition, the technique successfully cut down 70% training data while achieving the same recognition accuracy as conventional methods. We hope this technique might make further contribution to the protection of Chinese ancient works for libraries and archives in China.
This technique was presented on the “IS&T International Electronic Imaging Symposium 2017” held on January 31, Tuesday in San Francisco, USA.
Background
In China, there are about 50 million volumes of ancient books. They have a very high value of heritage and many of them are still attractive to the modern society. However, with the passage of time and the impact of human activities, these cultural heritage has been eroded and destroyed a lot.
In the preservation of ancient books, the libraries usually store them in the form of digital images. In addition to the protection of the literature, libraries also rely on ICT technology to make full use of the ancient literature by converting the data from character image to character code or text. At present, through the domain experts’ manual annotation, only a few of the ancient books have been completely digitized. To realize the digitization of all the ancient Chinese books, a lot of time and cost are needed.
Topics
In deep learning based character recognition, training data is of great importance which consists of huge number of text images and their associated text labels, so that the recognition engine can be trained sufficiently. Apparently, the more training data, the higher the recognition accuracy. However, as the number of character categories in ancient China is huge, the work of manually collecting and labeling character samples is not practical due to its prohibitively high cost and time consumption.
In contrast, the recognition of Alphabet letters and numbers can be achieved by collecting the training data in a relatively easy way since the number of characters is only a few. However, it is difficult to apply these techniques to the ancient Chinese literature in the form of a large number of fonts and different writing styles.
Technology
- Make full use of huge unlabeled character images and a small number of labeled training data
In order to increase the available training data, we utilize large number of character images which have not been used in the conventional training process as these images are not associated with correct character labels. As shown in Figure 1, recognition engine X gives each input character image a temporary label. In this step, due to inefficient training, these temporary labels may contain some errors as shown by the red characters in Figure 1.
- Compare the patterns of ‘same-label’ image pairs and the patterns of ‘different-label’ image pairs to improve the recognition engine
Extract a large number of sample pairs from the temporally labeled character image set and send them to the recognition engine Y and Z which share the same structure with recognition engine X. According to the comparison result that the input pair of images are associated with the same character or not, the recognition engine X is further refined. This process can be carried out iteratively. With more training iteration, the number of wrongly labeled character images is reduced and the accuracy of engine X increases. By the training of powerful recognition engine X, even with limited training data, the technique can achieve highly accurate recognition results.
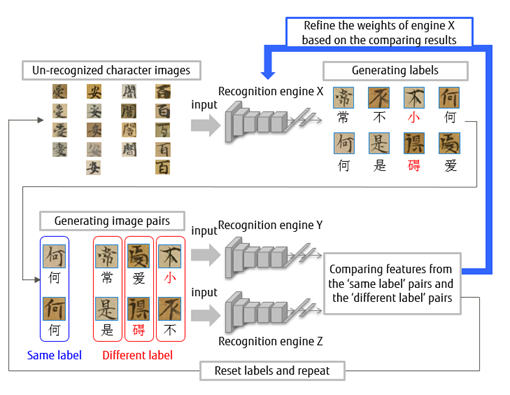
Figure 1: The developed character recognition framework
Effects
The developed technique was applied to 1000 historical document images of Dunhuang, China[2]. The results show that compared with the traditional techniques, only a small amount of training data is used to achieve the recognition accuracy of 81%. In average, the training data can be reduced by 70% for each character. Besides, when using 50 training samples per character, the technique achieves 88% recognition accuracy, while the previous released record in the academic society is 82%.
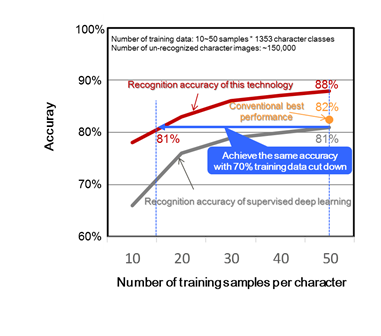
Figure 2: The effect of the developed character recognition technique applied to the Dunhuang dataset
Future plans
Fujitsu R&D Center will continually popularize our historical books digitization solution to the major Chinese local libraries and archives, promoting the integration of ancient books digitization, image retrieval and culture preservation. This technology can also effectively improve the recognition accuracy of Japanese, Korean and other languages. In order to be integrated effectively in 2018 Fujitsu AI platform 「Human Centric AI Zinrai」, we will continue to apply small sample based effective training technique to more object recognition fields, for example, the classification of a plurality of image data, the identification of plant species, etc.
Notes
![]() E-mail: hndwrt-recog@ml.labs.fujitsu.com
E-mail: hndwrt-recog@ml.labs.fujitsu.com

